Viewing and editing registry configuration
| 🌐 This document is available in both English and Ukrainian. Use the language toggle in the top right corner to switch between versions. |
1. Editing general settings
After successfully deploying your registry, you can view and edit its settings. You can do this in two simple steps:
-
Sign in to the Control Plane admin console as the registry administrator.
-
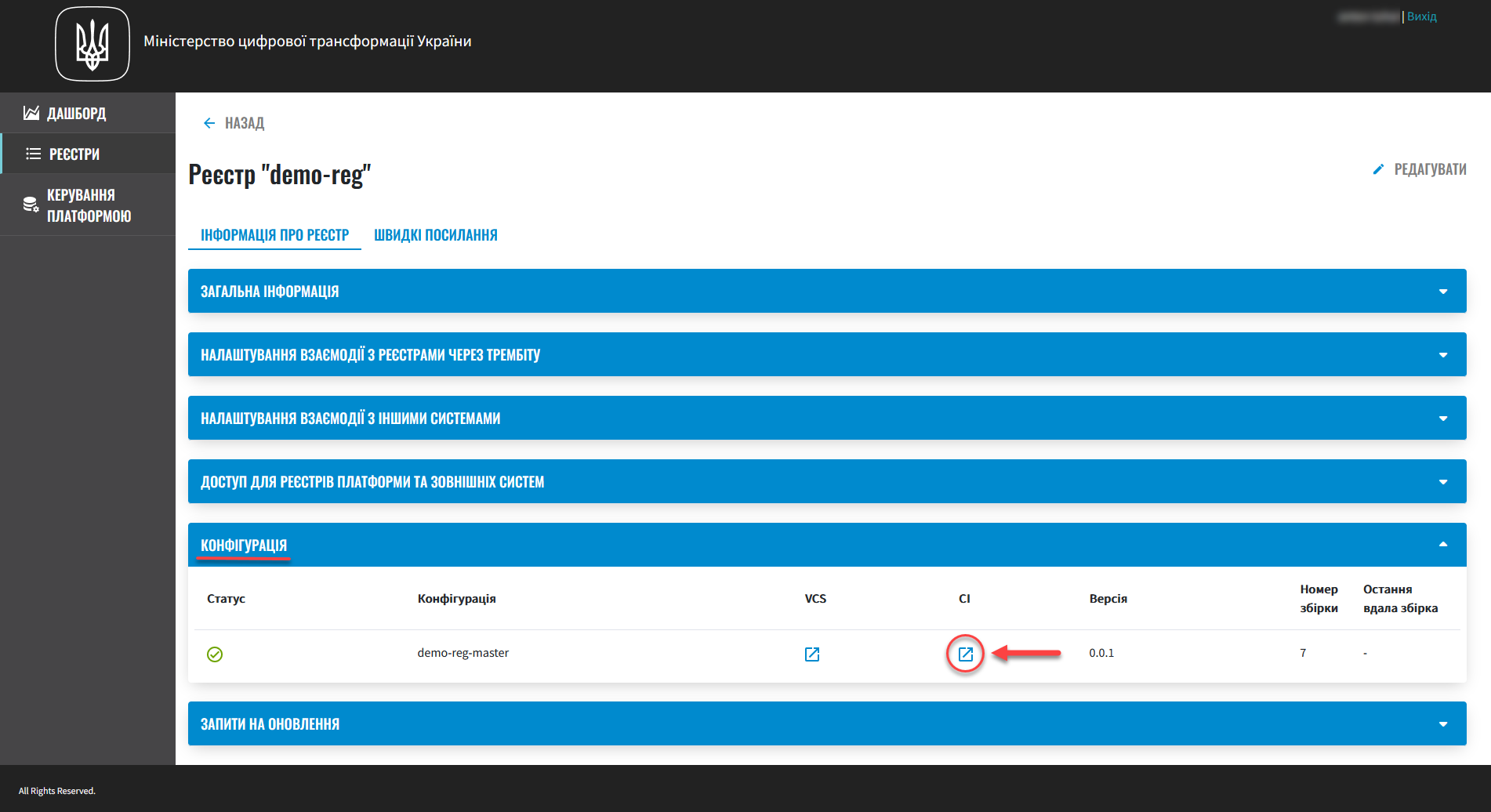
Open the Registries section, find the registry you wish to edit, and click the edit icon (🖉).
As a result, the Edit registry page opens. Here you can update the following settings:
| Updating the registry configuration follows the GitOps approach, similar to the deployment process. |
You can open the Edit registry page either from the list of registries (using the edit icon) or the registry details page (using the Edit button in the upper-right corner).
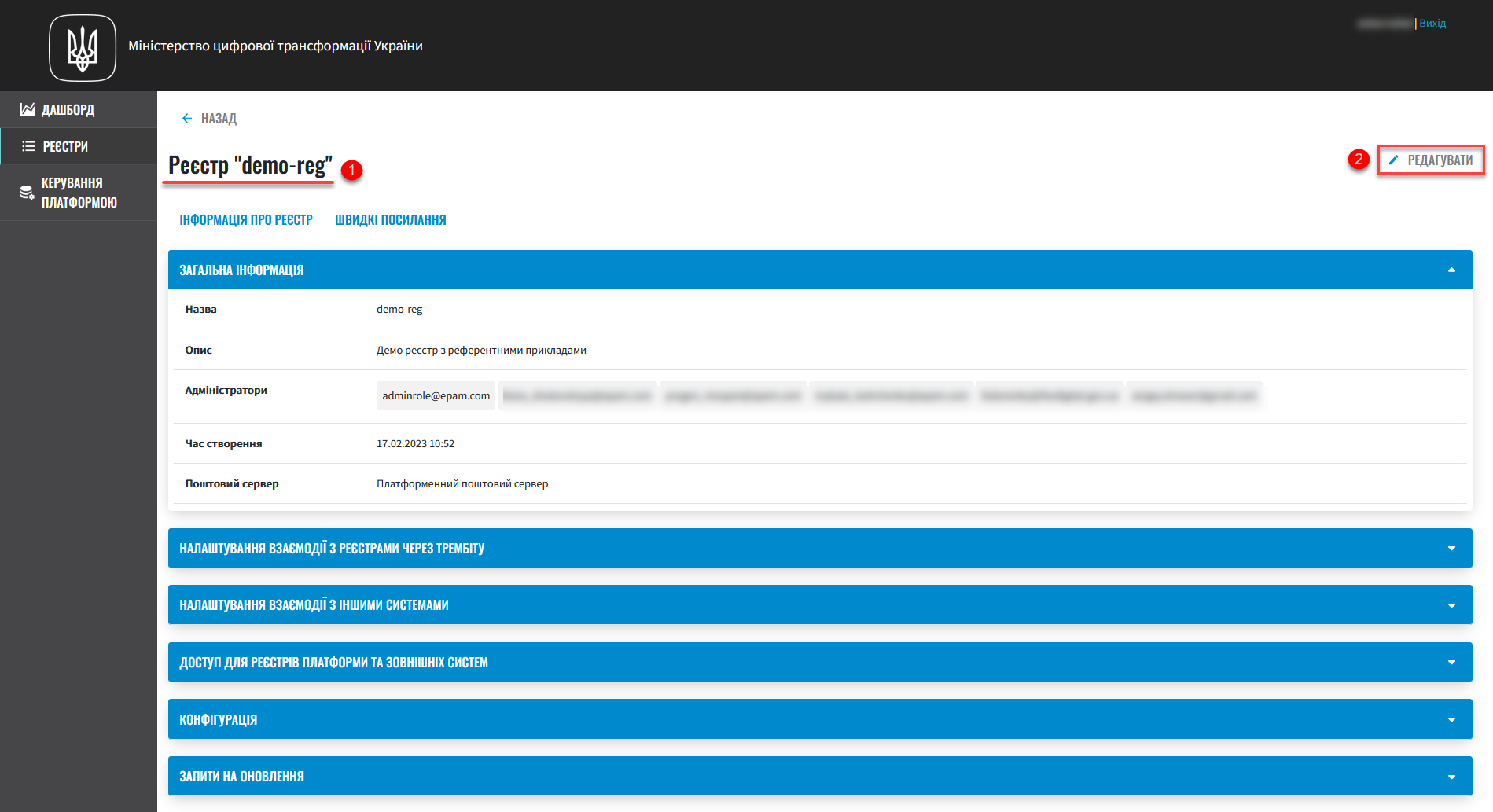
2. Viewing registry details, access settings, and external integrations
You can view basic information about the registries deployed on the Platform, manage access to your registry, configure external SOAP or REST integrations, view registry configuration, and approve or reject configuration update requests.
-
Sign in to the Control Plane admin console as the registry administrator.
-
Go to the Registries section and click the name of your registry.
The registry details page contains two tabs:
-
Registry information
-
Quick links
- This tab contains the following sections:
-
-
General information. You can view and edit it if needed.
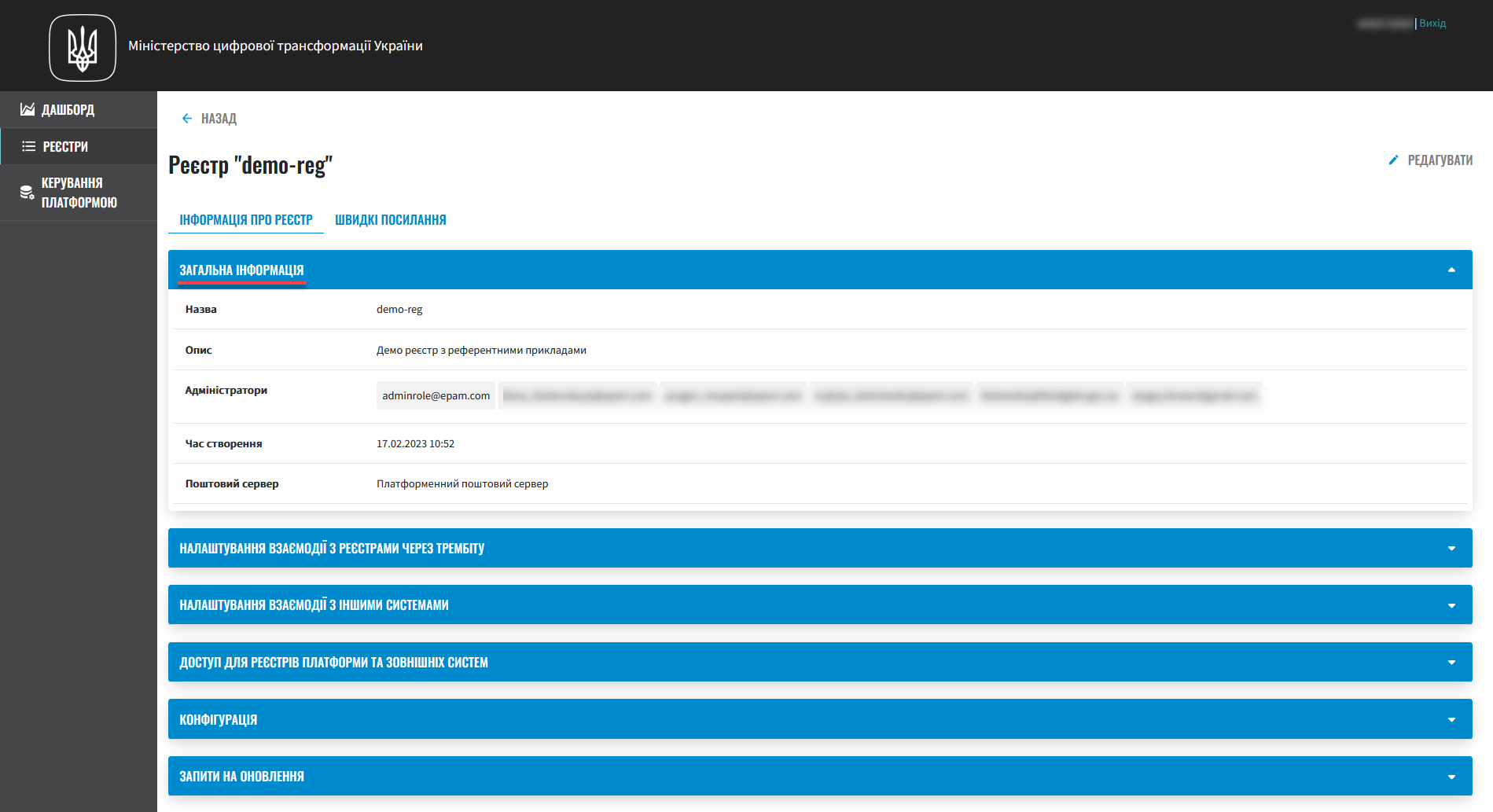
The registry name cannot be changed. -
Setting up interaction with registries via Trembita. You can set up interaction with other registries that are part of the SEI SEIR Trembita system via the SOAP protocol.
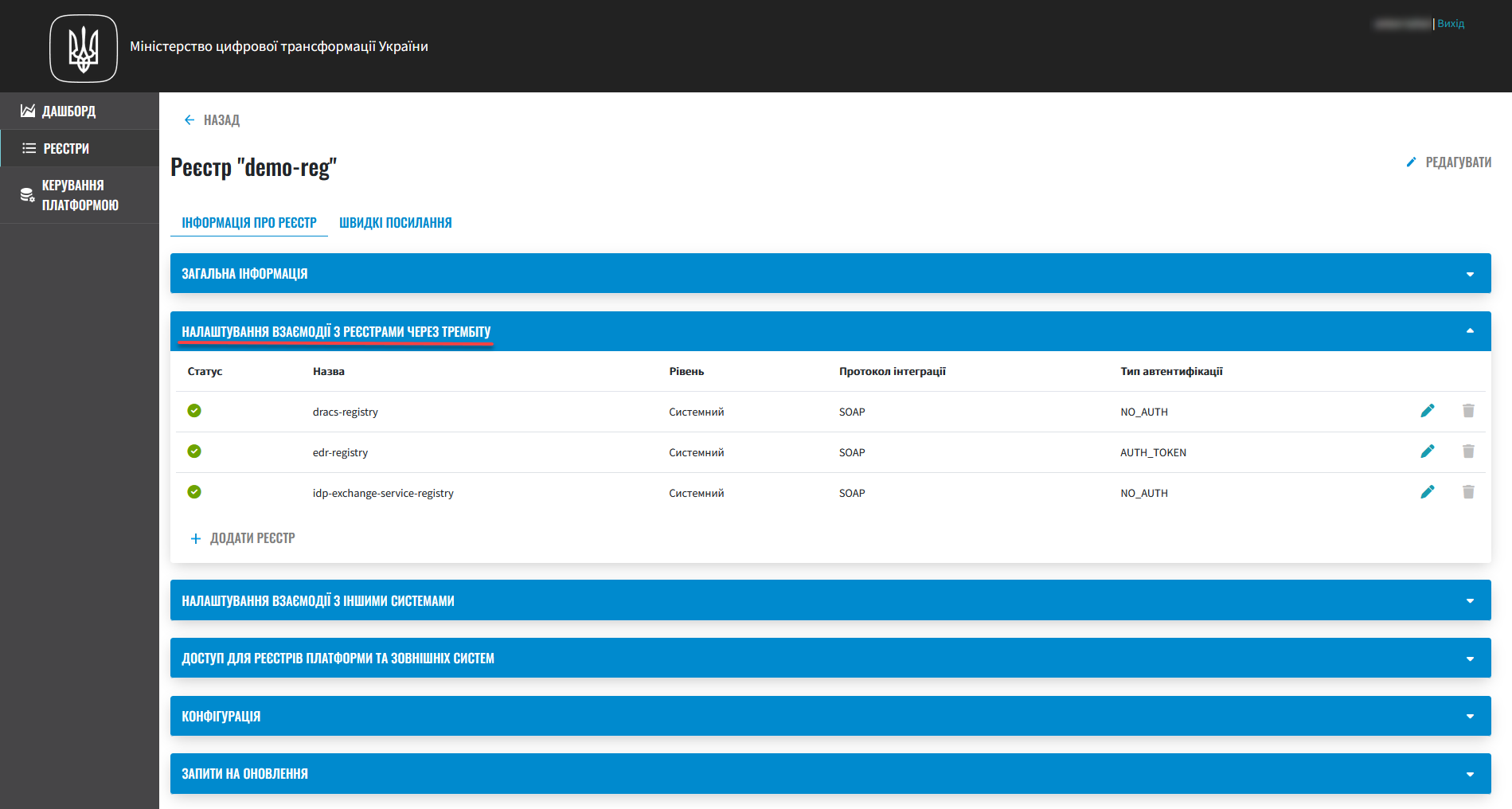
-
Setting up interaction with other systems. You can set up interaction with other registries and external systems via the REST protocol.
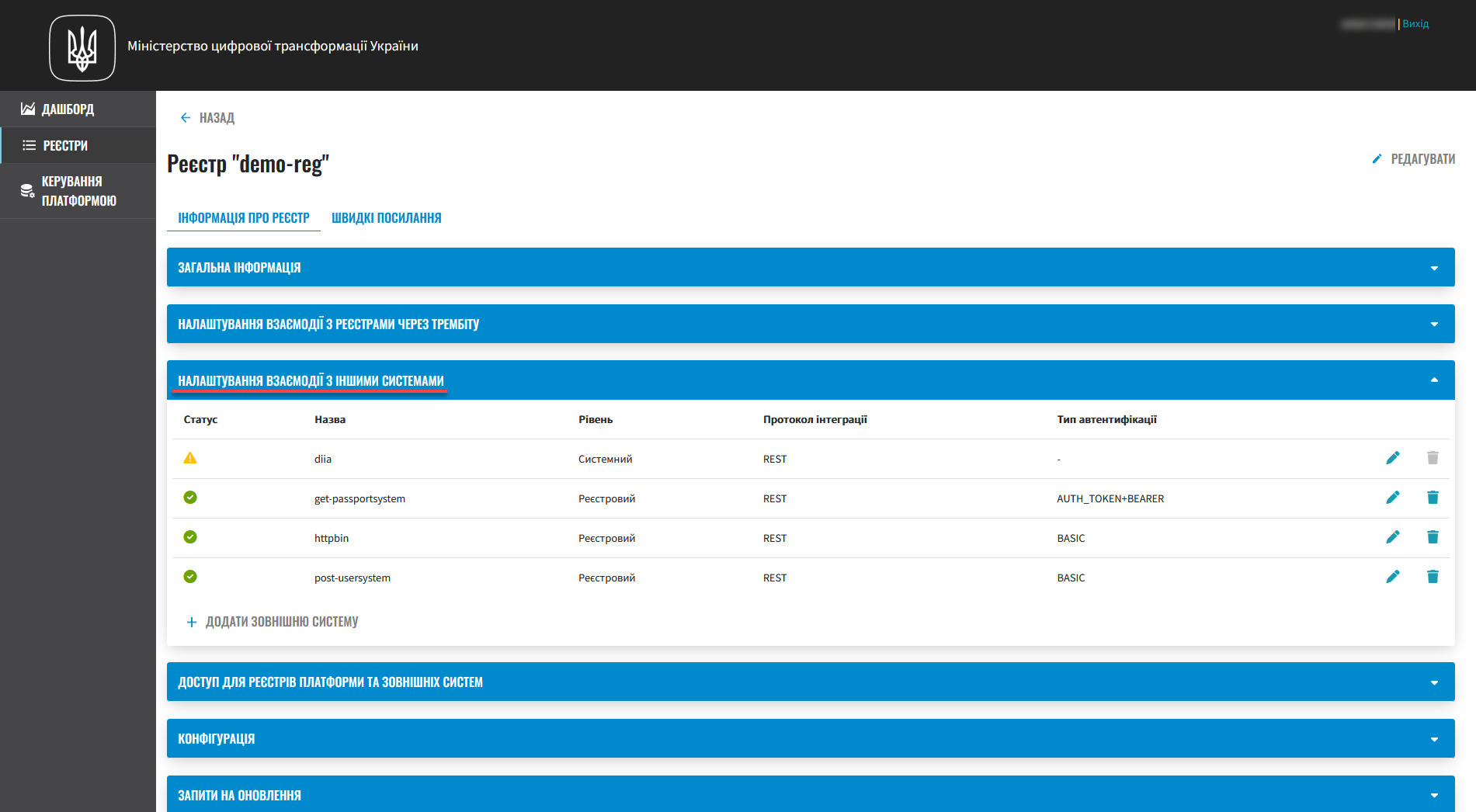
For details, see Configuring integrations with external systems in Control Plane. -
Access to Platform registries and external systems. You can configure access to your registry for other registries on the Platform or external systems.
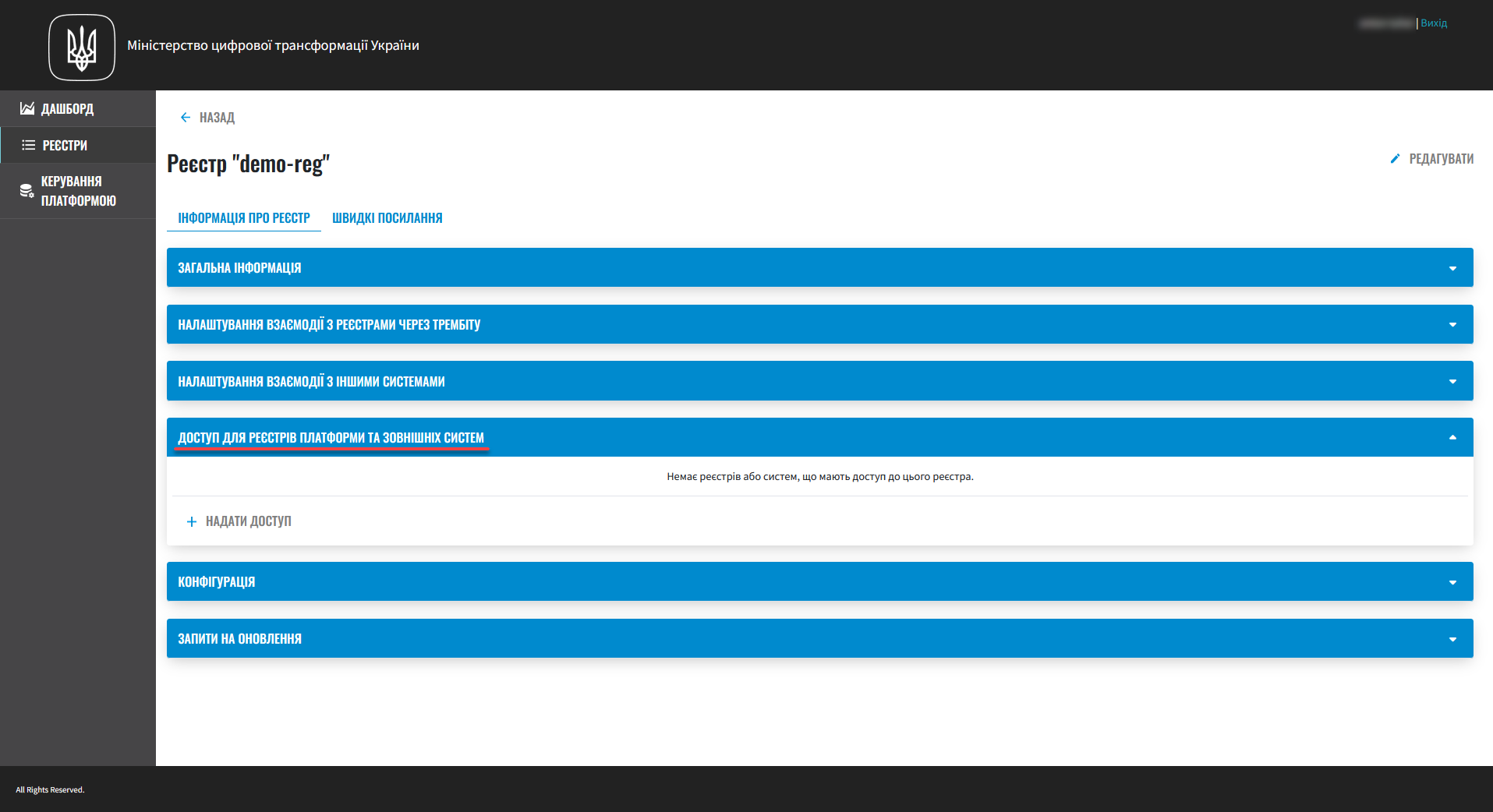
For details, see Configuring registry access. -
Configuration. This section contains the following links:
-
Update requests. You can change your registry configuration by editing any of its settings. These changes go to the Update requests section, where you can review and either approve or reject them.
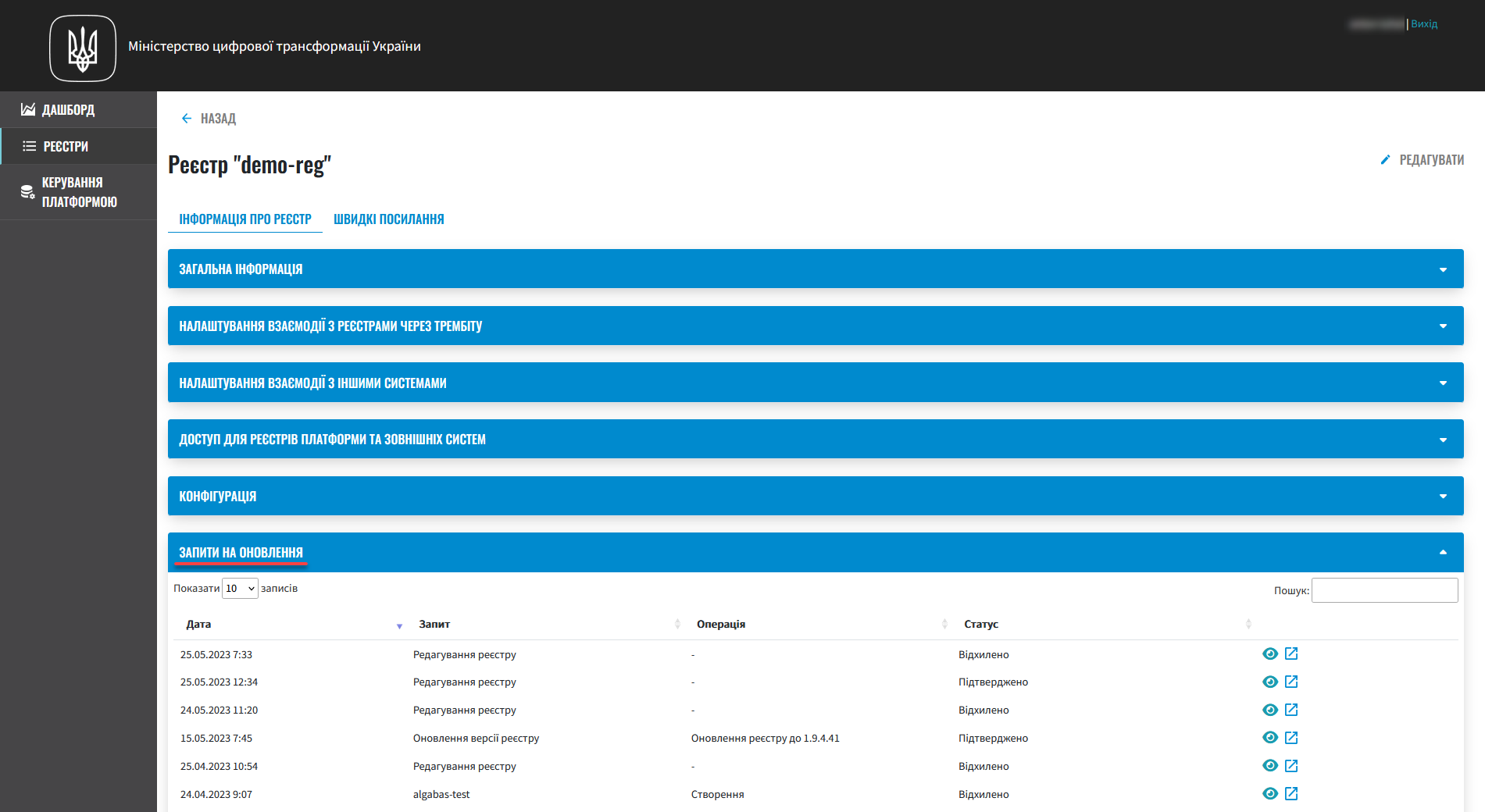
-
This tab contains links to the web interfaces of the various services with brief descriptions.
For details, see Quick links to registry services. -
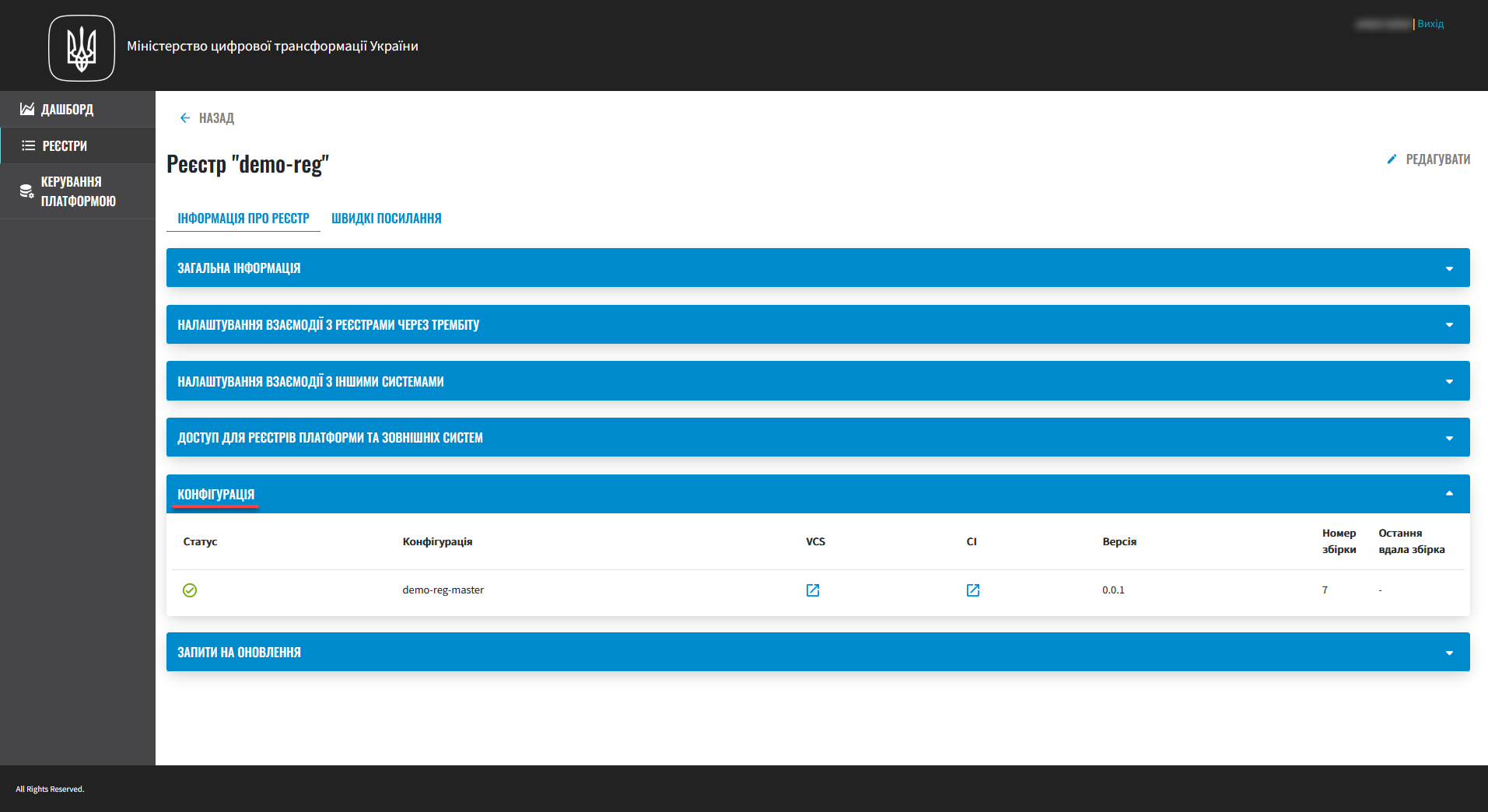
3. Monitoring the deployment of changes
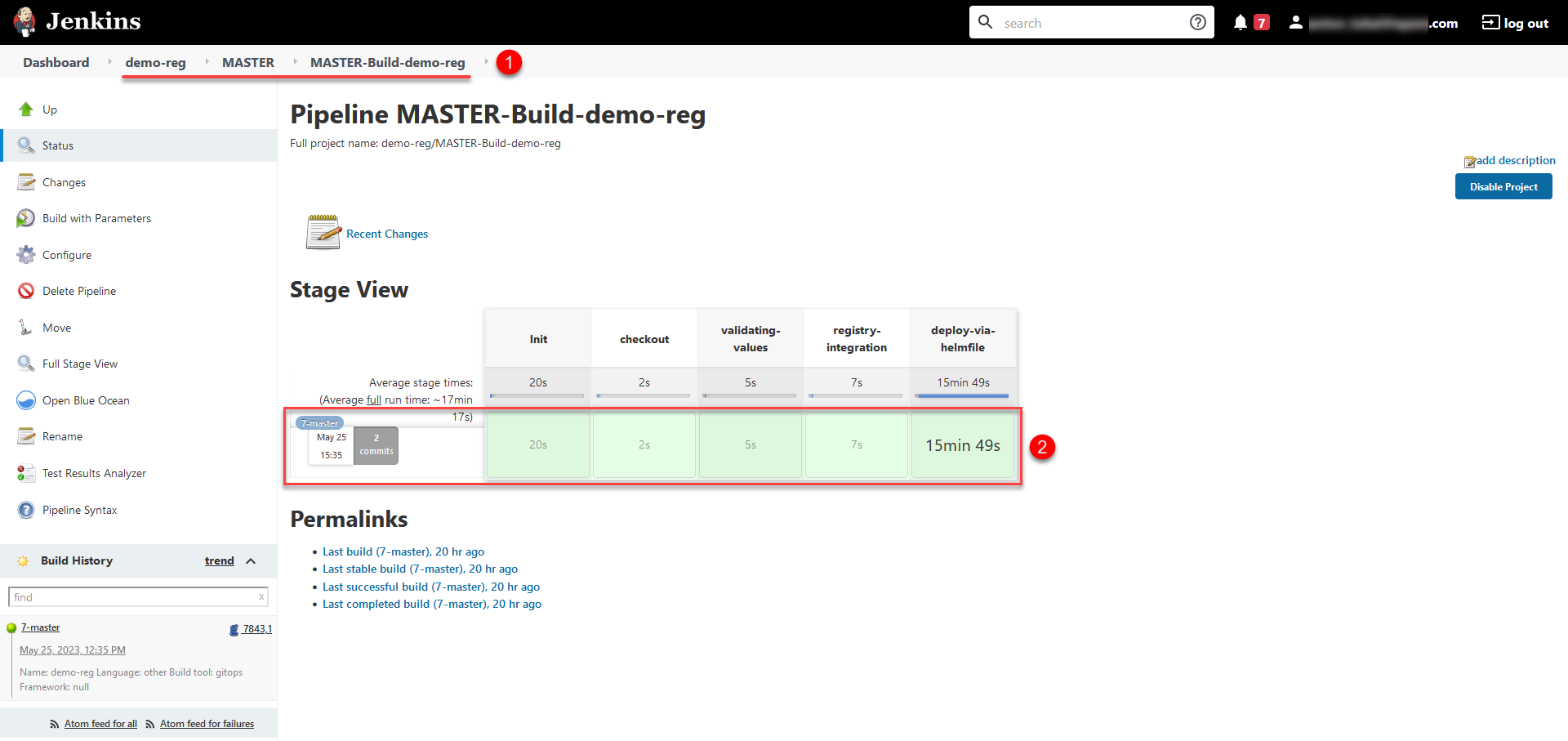
Deploying configuration changes takes some time. The Jenkins service starts the deployment automatically by running the Master-Build-<registry-name> pipeline, where <registry-name> is the name of your registry. To monitor the deployment process, go to the Registries section and open the registry you modified, then scroll down to the Configuration section and click the Jenkins link icon in the CI column.
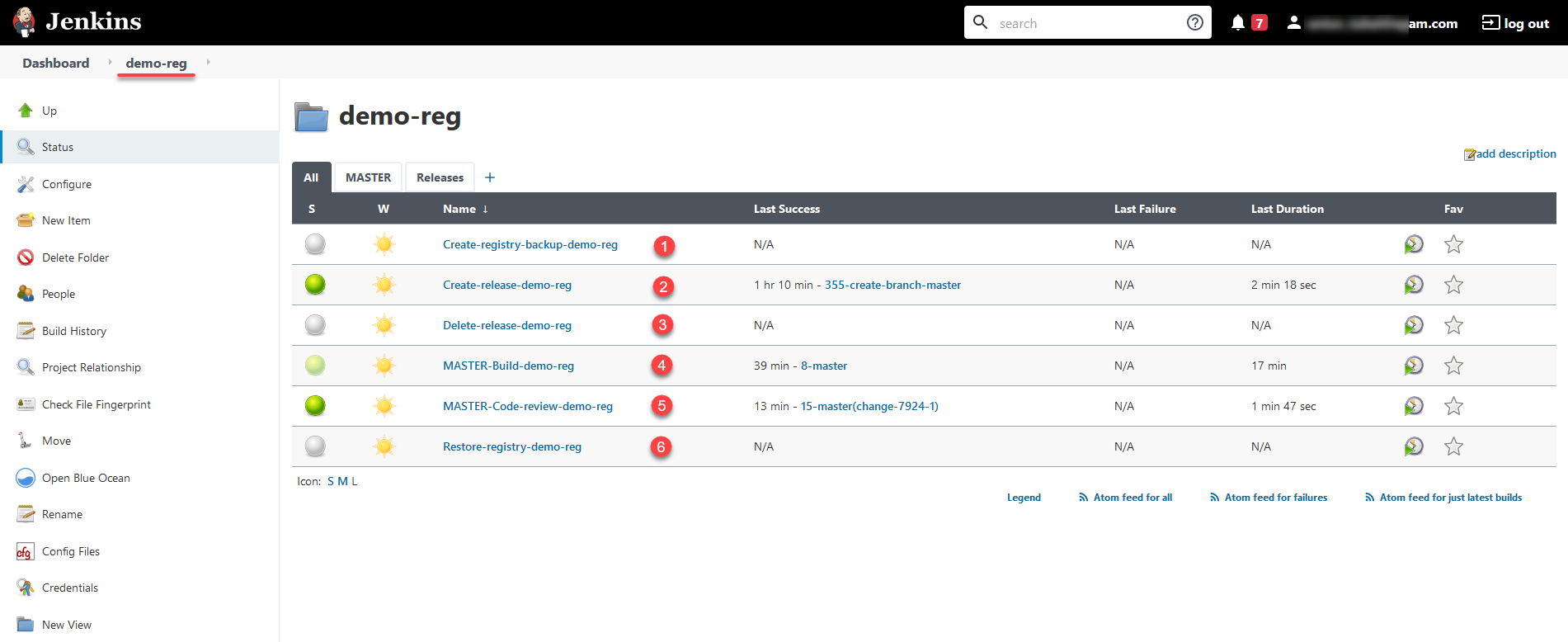
The central Jenkins component provides several out-of-the-box processes (pipelines):
- Service processes
-
Service processes perform various auxiliary functions and set the stage for the main pipelines. These include:
-
Create-release-
<registry-name>performs several service operations, including cloning the repository and creating a new branch. Starts a service pipeline namedjob-provisions>ci>default-<codebase.version>(where<codebase.version>is the version number of the build that corresponds to the Git tag in Gerrit), which prepares the stage for the subsequent CI/CD process. -
MASTER-Code-review-
<registry-name>is a system process of code quality review that is launched automatically viagit pushto themasterbranch of the Gerrit repository.
-
- Main processes
-
Main processes build the code used to deploy various functional components of the registry. These include:
-
Master-Build-
<registry-name>is the primary code build process for deploying or updating the registry configuration. This includes resource allocation, deployment of registry services such as user portals, Business Process Management System (BPMS), database, data factory components, empty regulations deployment, and so on. -
Create-registry-backup-
<registry-name>is a process that creates registry backups and puts them in the MinIO object storage. -
Restore-registry-
<registry-name>is a process that enables you to create (restore) a registry from a backup copy. -
Delete-release-
<registry-name>is a process that enables you to delete a registry.
-