Expanding space for Elasticsearch
| 🌐 This document is available in both English and Ukrainian. Use the language toggle in the top right corner to switch between versions. |
This document provides the following instructions:
-
Adding storage capacity to your EFK (Elasticsearch, Fluentd, and Kibana) stack.
-
Dropping indexes to optimize disk space.
1. Adding storage capacity to Elasticsearch
If you run out of disk space for Elasticsearch and need to expand it, follow these steps:
-
Sign in to the Openshift console of the corresponding cluster, find the
openshift-loggingproject, and open Persistent Volume Claims.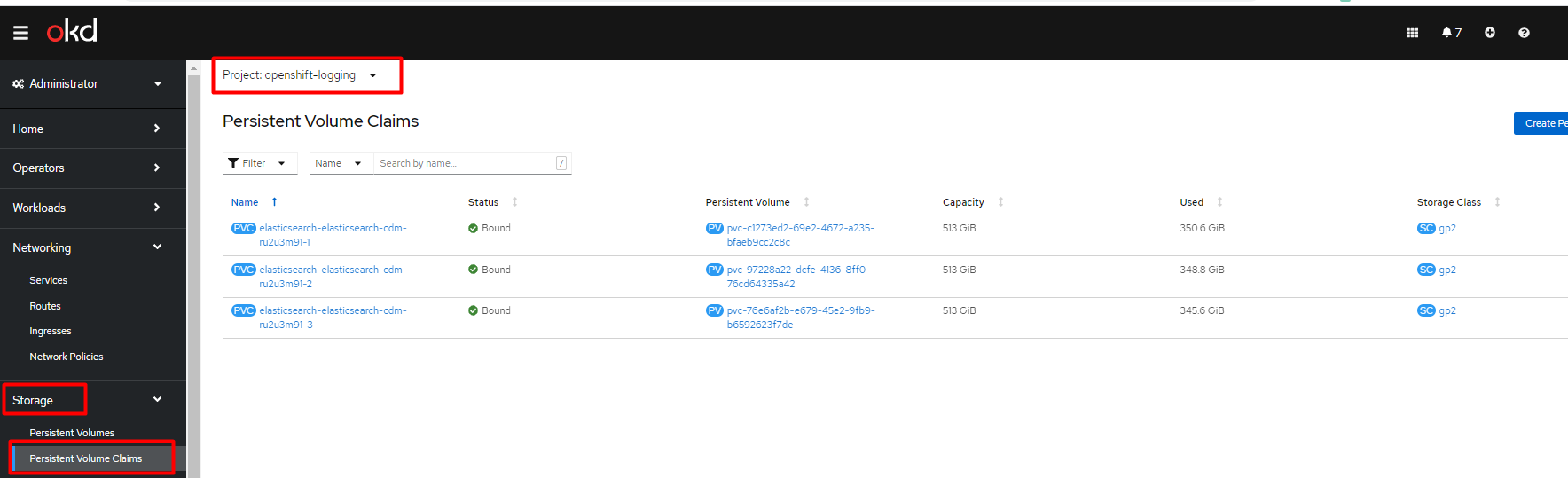
-
Expand the actions menu of a PVC and click
Expand PVC.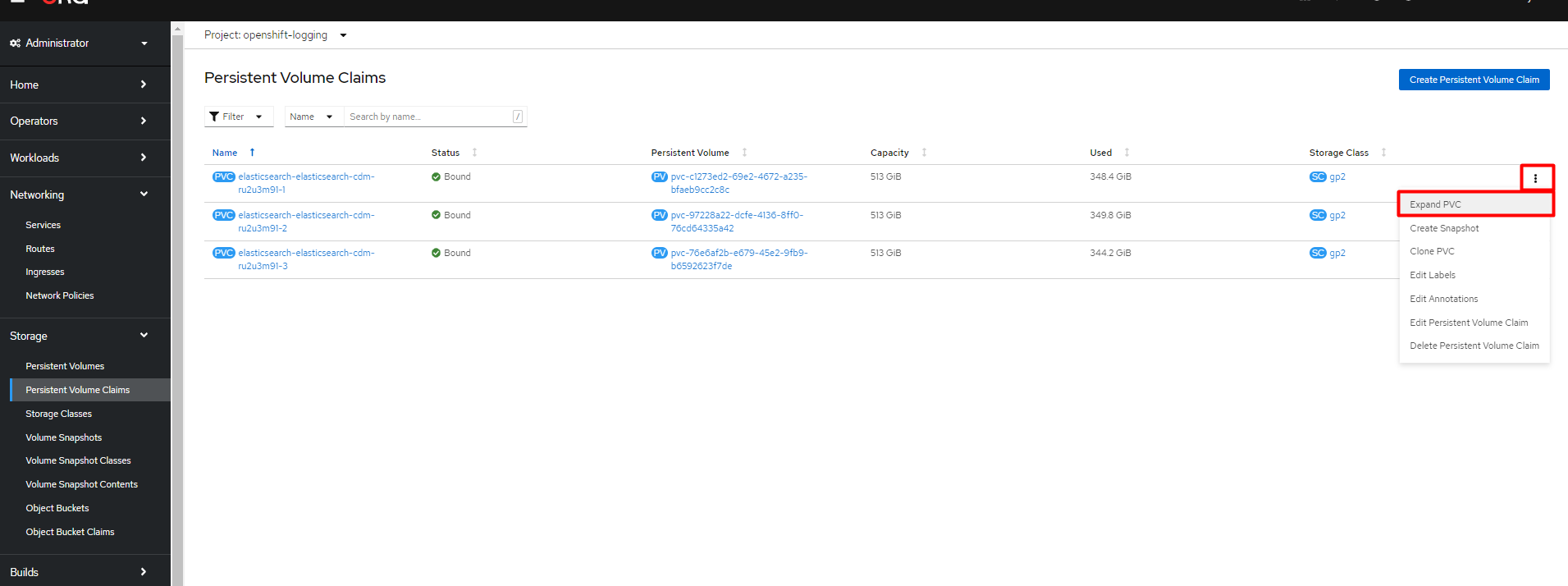
-
In the Expand PersistentVolumeClaim window, specify the desired disk size and click
Expand.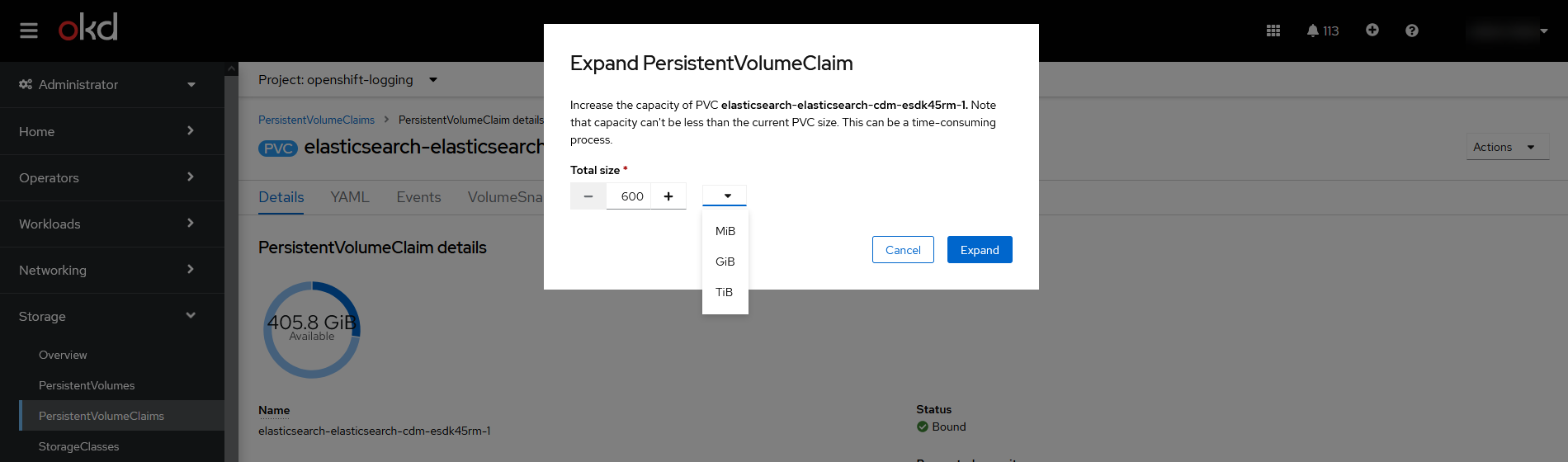
-
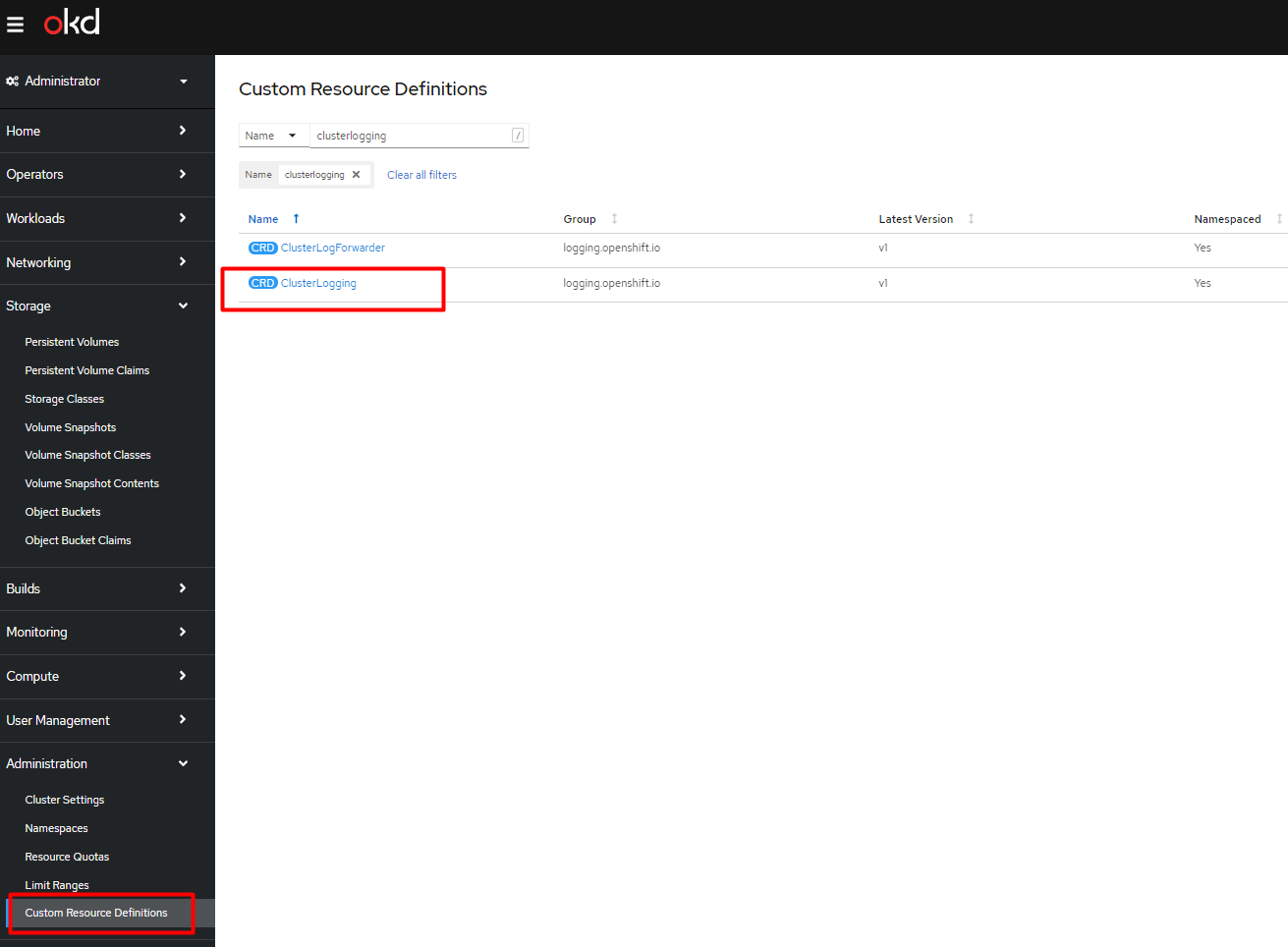
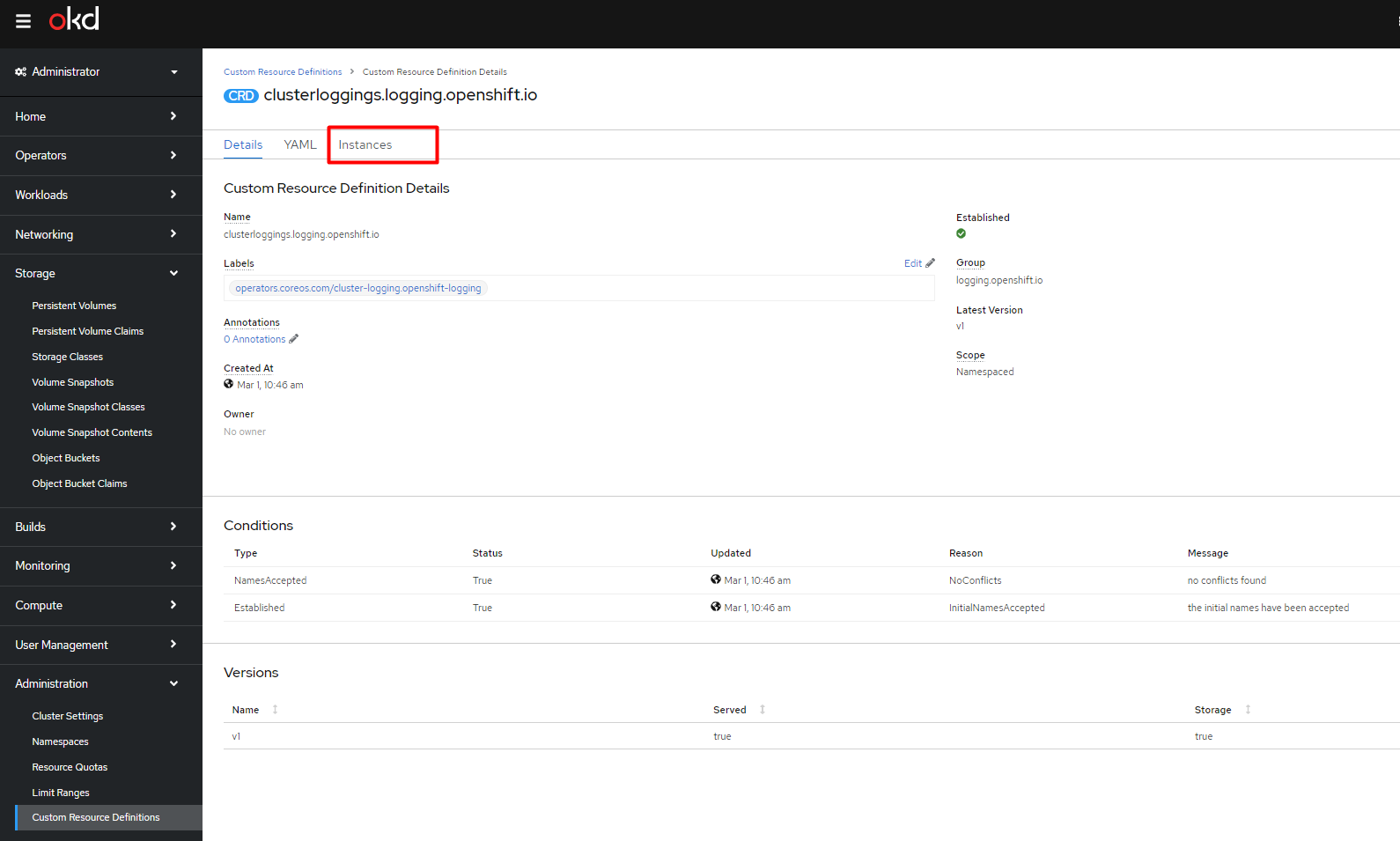
Go to Administration > Custom Resource Definitions and find the ClusterLogging CRD.
-
Open ClusterLogging and switch to the Instances tab.
-
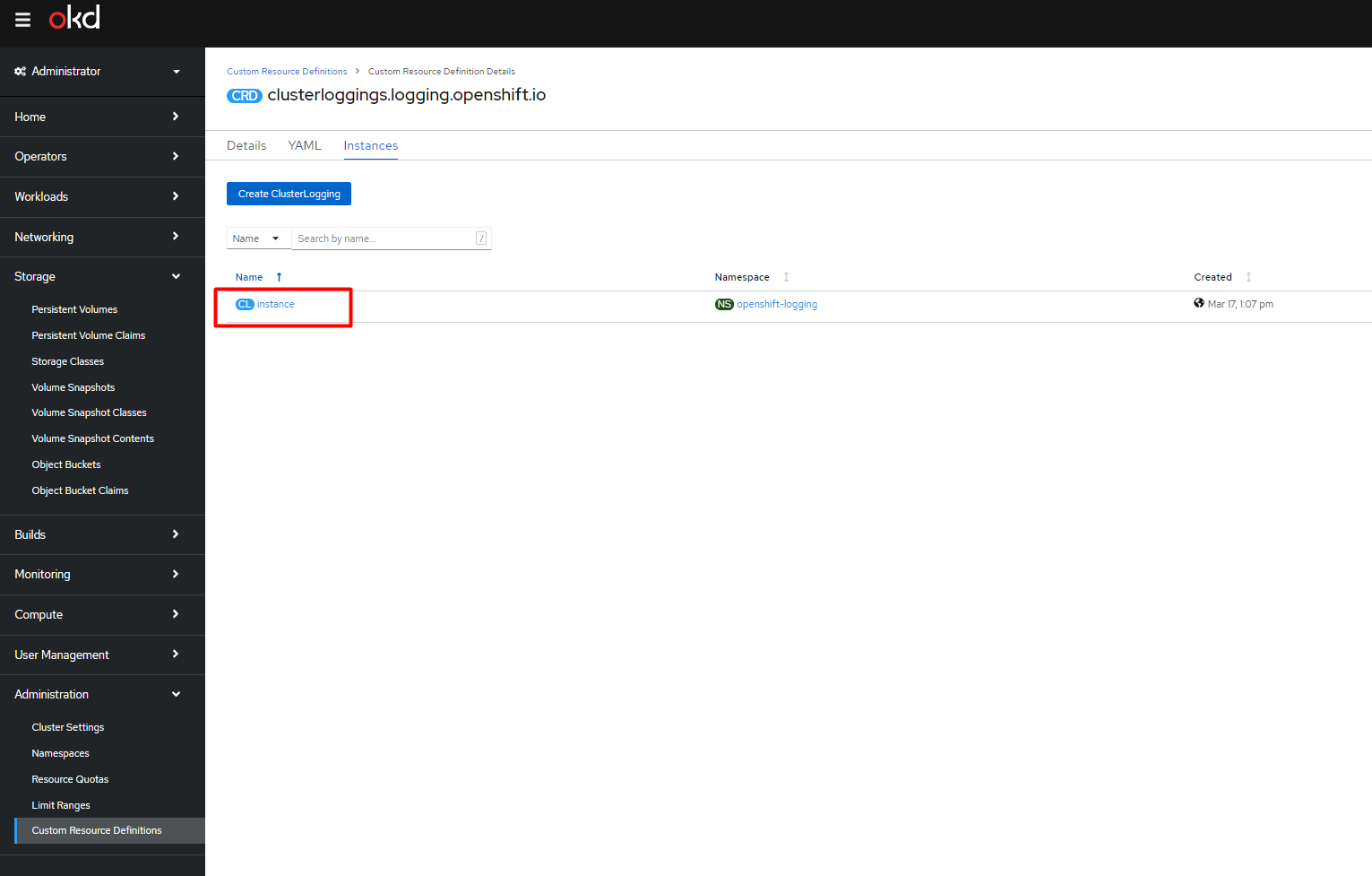
Click the Instance link for the openshift-logging project.
-
Open the YAML tab and find the
storage.sizeparameter. Change the disk size to the one you set in the Expand PersistentVolumeClaim window.Cluster Logging instance YAML example
storage: size: 600G storageClassName: gp2 tolerations: - effect: NoSchedule key: platform/logging operator: Equal value: 'true' retentionPolicy: application: maxAge: 5d audit: maxAge: 5d infra: maxAge: 5d type: elasticsearch managementState: Managed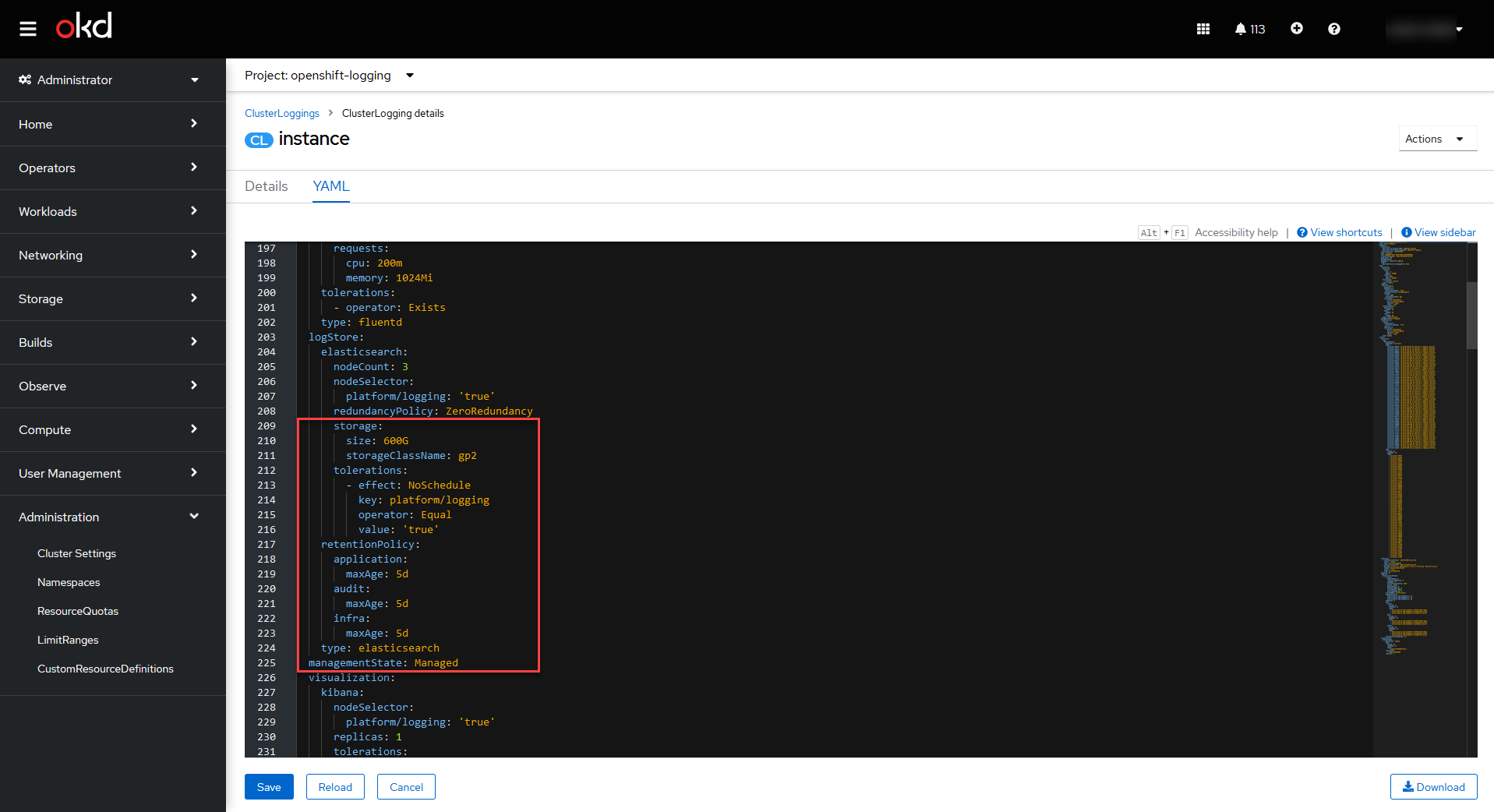
-
Click
Saveto save your changes.
2. Dropping Elasticsearch indexes
If you need to drop Elasticsearch indexes, perform the following steps:
-
Sign in to the Openshift console of the corresponding cluster, find the
openshift-loggingproject, and go to Workloads > Pods.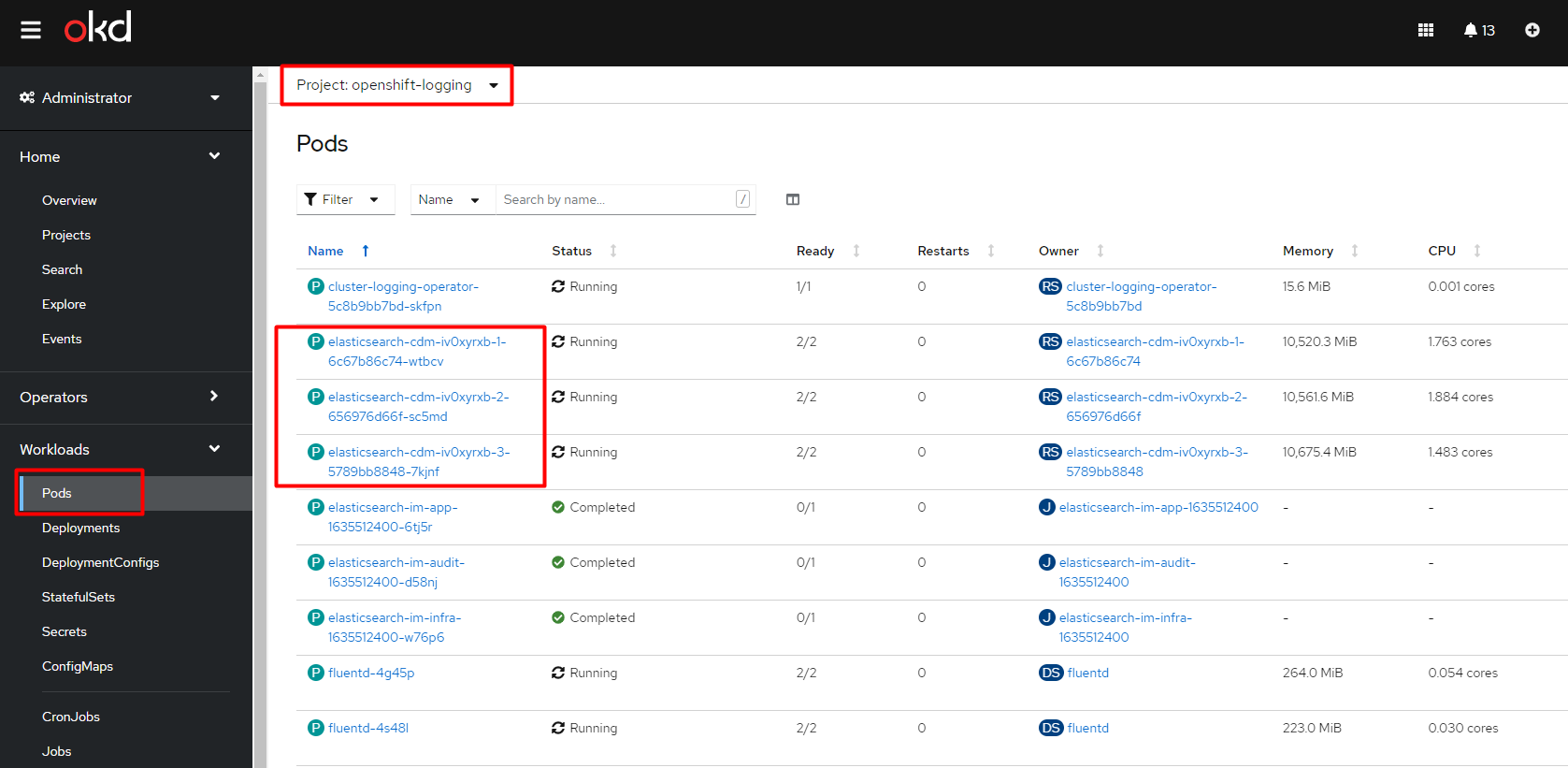
-
Open one of the three
elasticsearch-cdm-iv…pods and switch to the Terminal tab.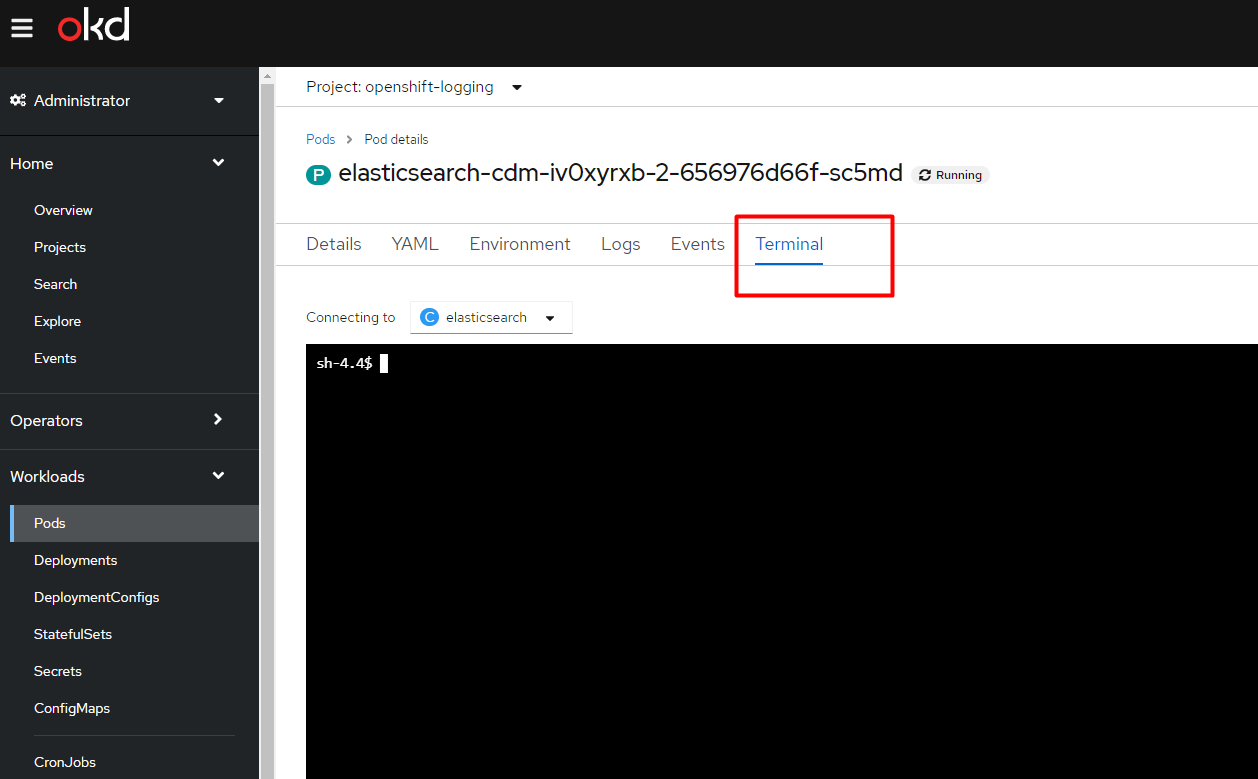
-
View a list of all available indexes. To do this, use the following command:
curl -XGET -s --cacert /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-ca --cert /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-cert --key /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-key -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?h=h,s,i,id,p,r,dc,dd,ss,creation.date.string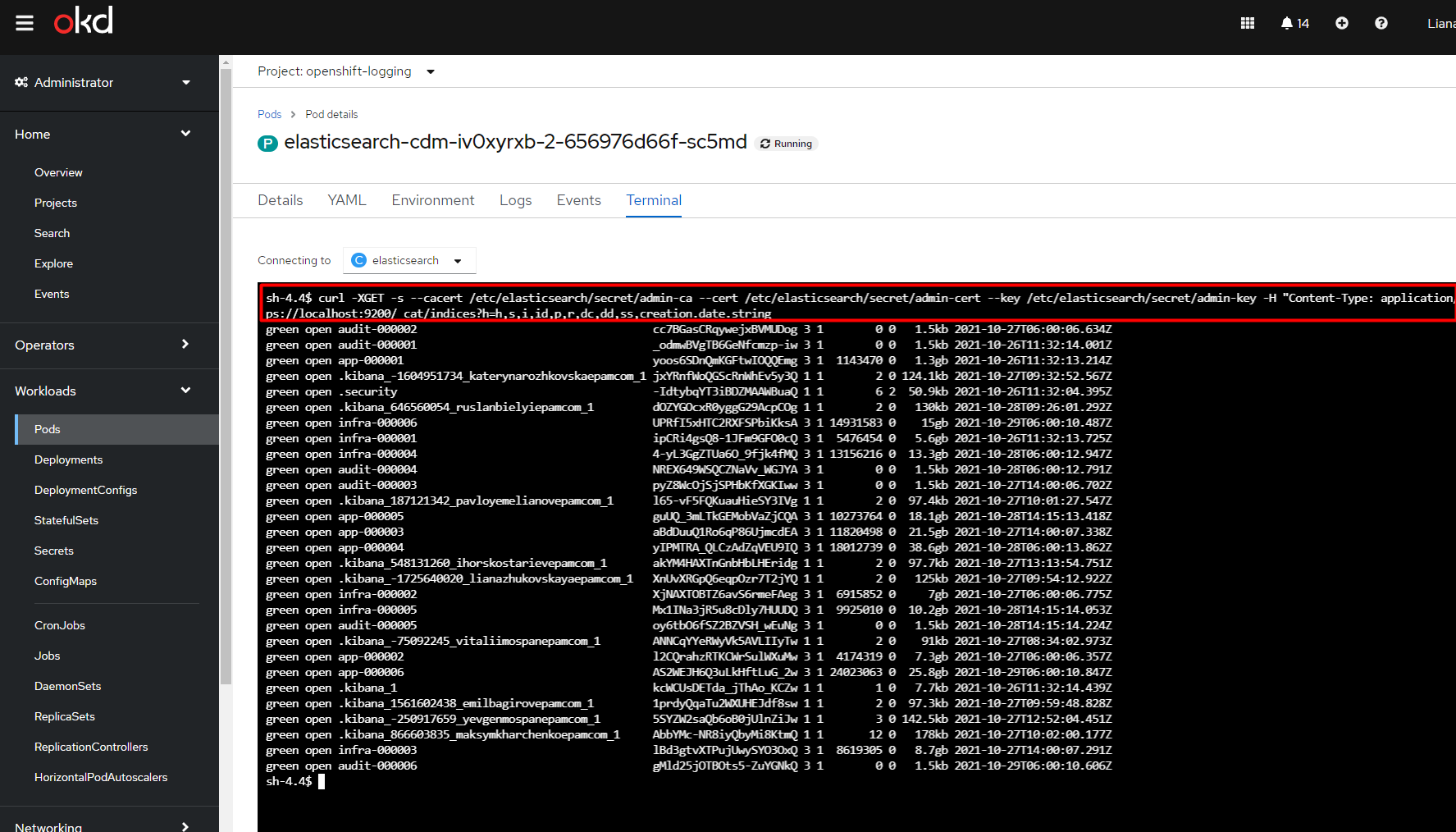
-
Select the index you want to delete.
For example, let’s delete the
infra-000004index. To do this, use the following command:curl -s --cacert /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-ca --cert /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-cert --key /etc/elasticsearch/secret/admin-key -XDELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://localhost:9200/infra-000004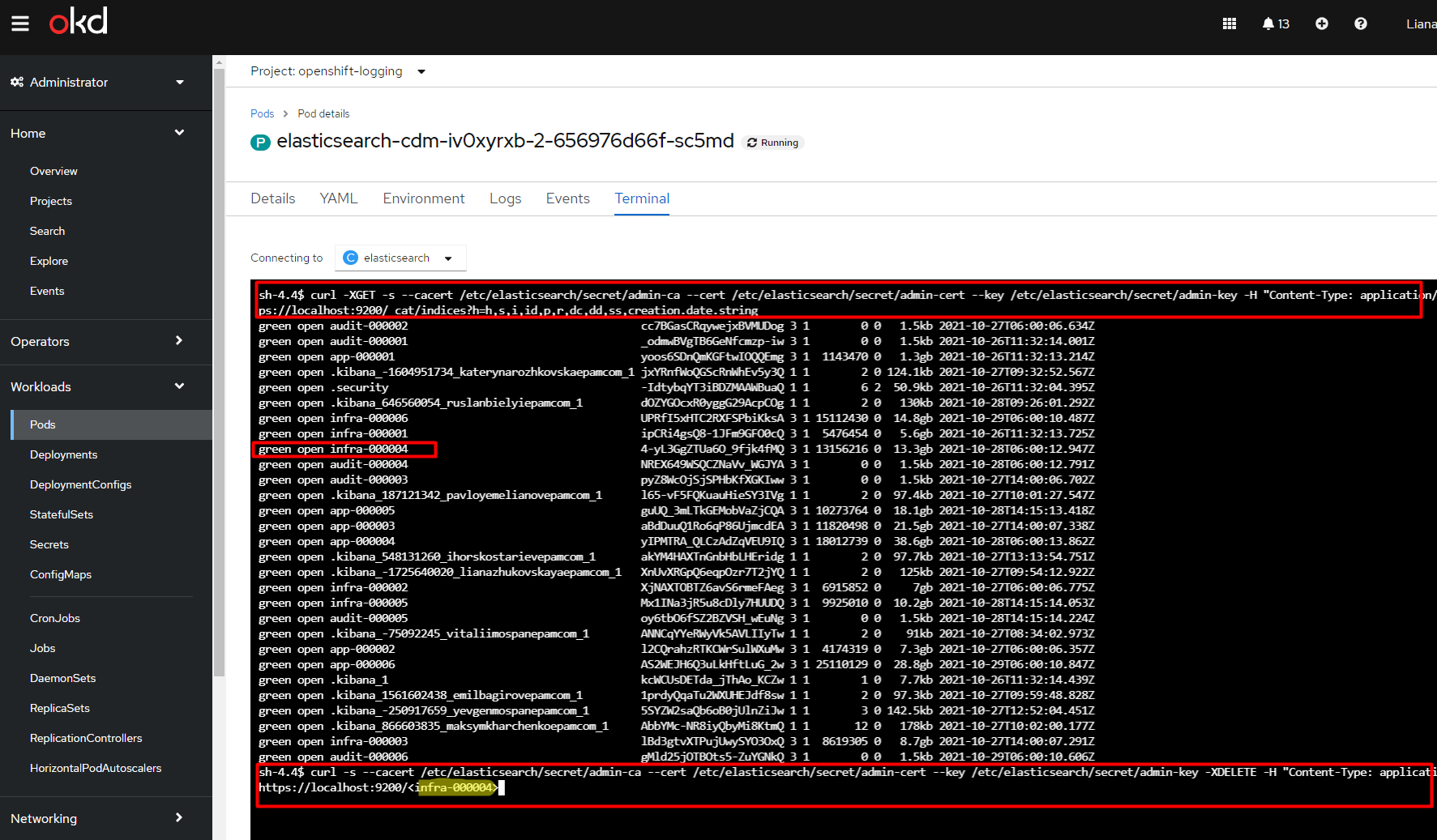
All previously created indexes will also be deleted, while others will remain intact.