Registry regulations cleanup
| 🌐 This document is available in both English and Ukrainian. Use the language toggle in the top right corner to switch between versions. |
1. Overview
The cleanup pipeline (cleanup-job) in Jenkins is an automated process designed to optimize the registry regulations by removing obsolete or unnecessary data, resources, and components. The process performs the following tasks:
-
Cleaning up temporary DB replicas deployed for version candidates.
-
Removing resources and services.
-
Cleaning up the Nexus repository.
-
Additional cleanup operations set up by an administrator.
| We do not recommend running the cleanup job on production environments, as this may result in the loss of important data. |
2. Cleanup job stages and steps
The cleanup process includes the following stages:
- cleanup-of-version-candidate-dbs
-
During this stage, the job cleans up temporary databases for version candidates, which frees up disk space and helps to keep the system in order.
For details on deploying the databases for version candidates, see registry-admin/admin-portal/registry-modeling/tables/tables-data-structures.adoc#data-model-version-candidate. - delete-data-services
-
During this stage, the job removes
buildConfigand Helm chart resources for the following data services:registry-kafka-api,registry-soap-api,registry-rest-api, andregistry-model. Also, the job removes Kafka topics for the registry API service (registry-rest-api).Data services are services and tools that enable data collection, processing, storage, and provision for various applications, users, and systems.
- cleanup-trigger
-
This stage contains several steps:
-
Deleting the following data services:
registry-kafka-api,registry-soap-api,registry-rest-api, andregistry-model. -
Deleting
history-excerptor.History excerptor is a tool that generates a readable excerpt with changes from a history table containing data about changes in all other registry database tables and enables downloading this excerpt in PDF format directly from the Jenkins console.
-
Cleaning up the Nexus artifacts repository.
-
One of the following options:
-
Deleting the registry regulations repository (
registry-regulations) and cleaning the Redash database and resources (if theDELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYcheckbox is selected). -
Leaving
registry-regulationsunchanged and cleaning the Redash database and resources (if theDELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYcheckbox is cleared).
-
-
Creating new empty repositories for
history-excerptorandregistry-regulations.Creating registry-regulationsis skipped if the cleanup process did not remove this component. -
Starting the
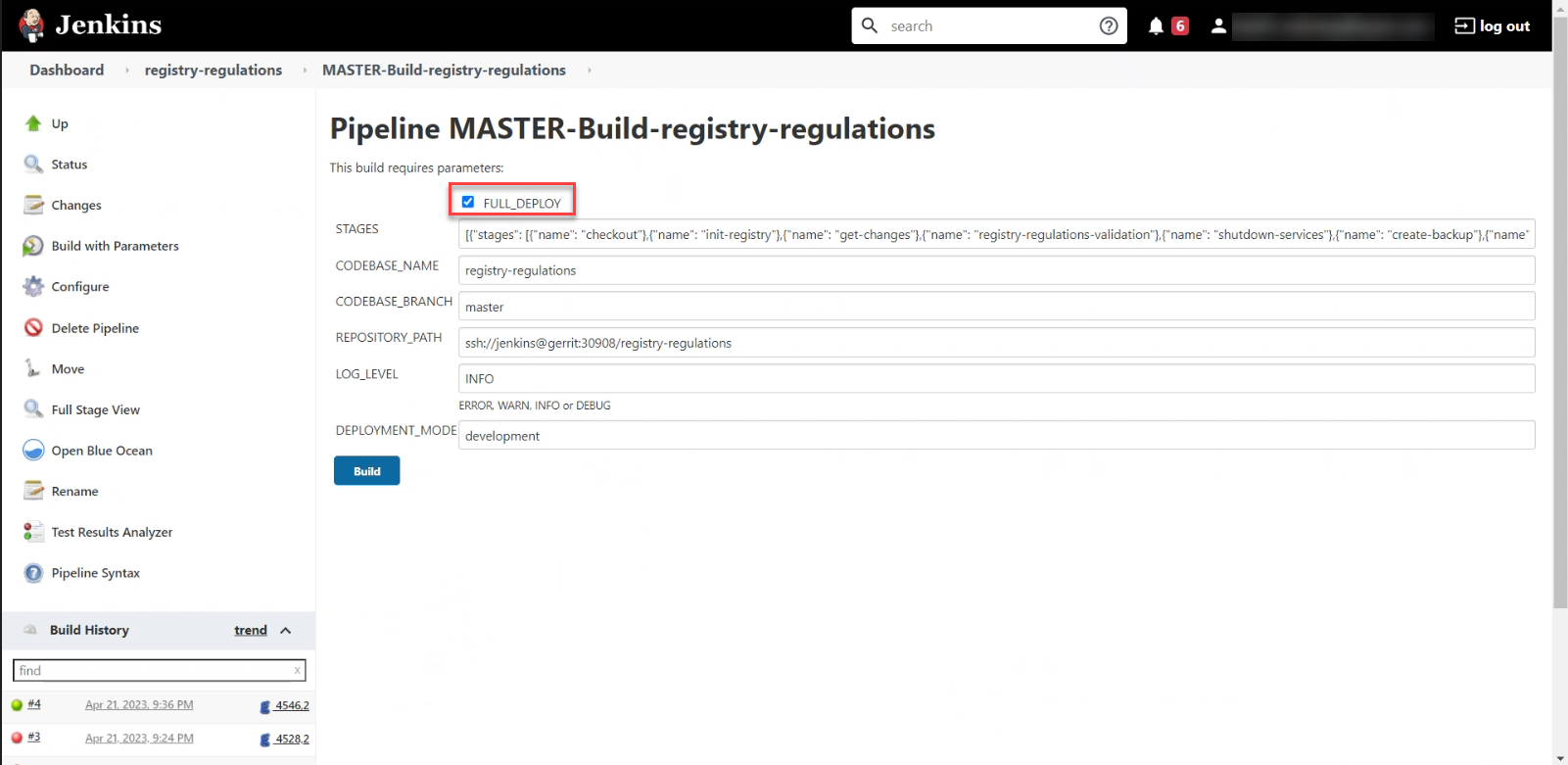
MASTER-Build-registry-regulationspipeline with theFULL_DEPLOYoption (provided that the cleanup process did not remove theregistry-regulationscomponent), which allows deploying the regulations correctly after the cleanup process.
3. Configuring and starting the cleanup process
You can configure and start the regulations cleanup process in the registry Jenkins service using the following link: https://admin-tools-<registry-name>.apps.<cluster-name>.dev.registry.eua.gov.ua/cicd
-
Sign in to the Control Plane admin console.
-
Go to Registries > Quick links and click the Jenkins service link.
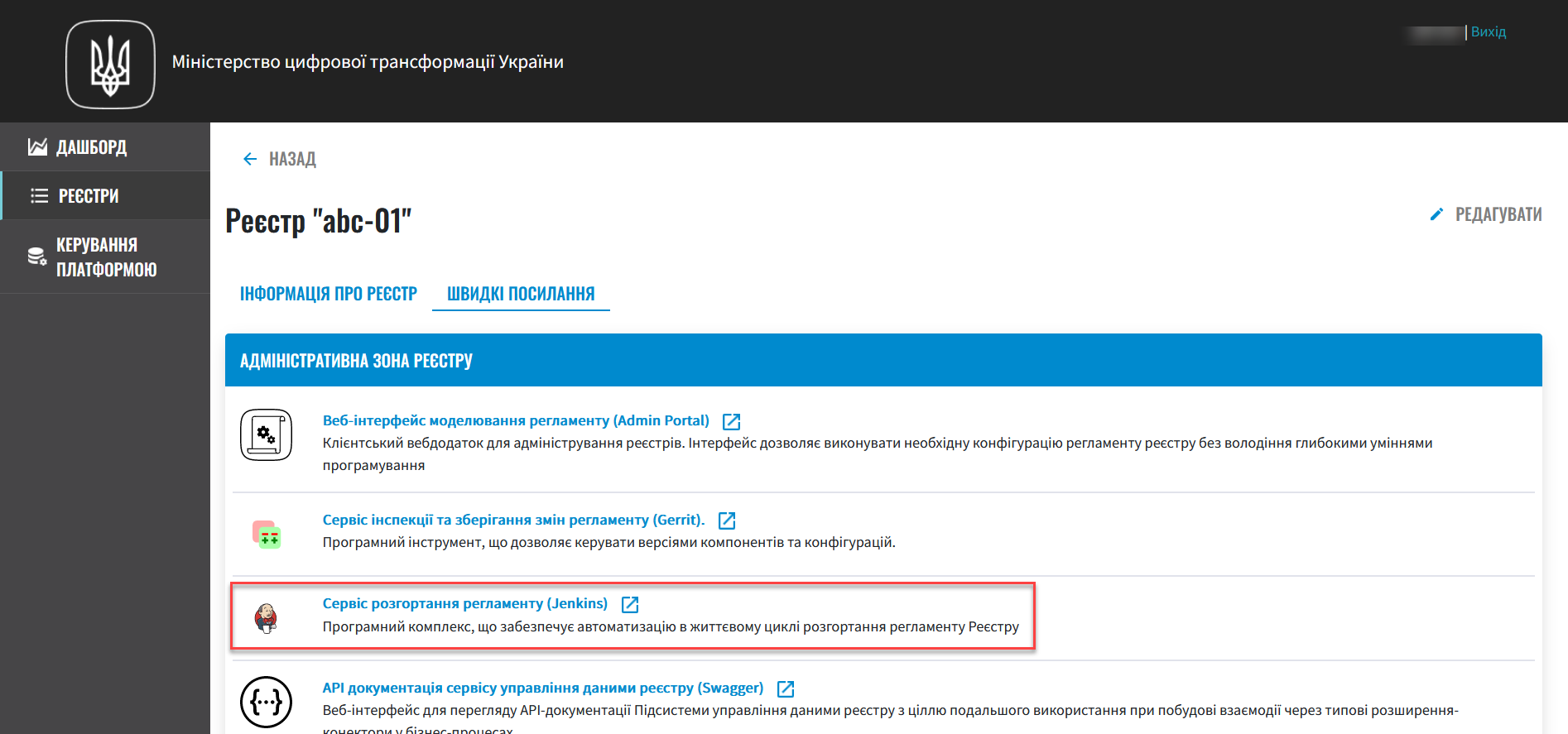
For details, see Quick links to registry services. -
Open the
cleanup-jobpipeline and clickBuild with Parametersin the leftmost menu.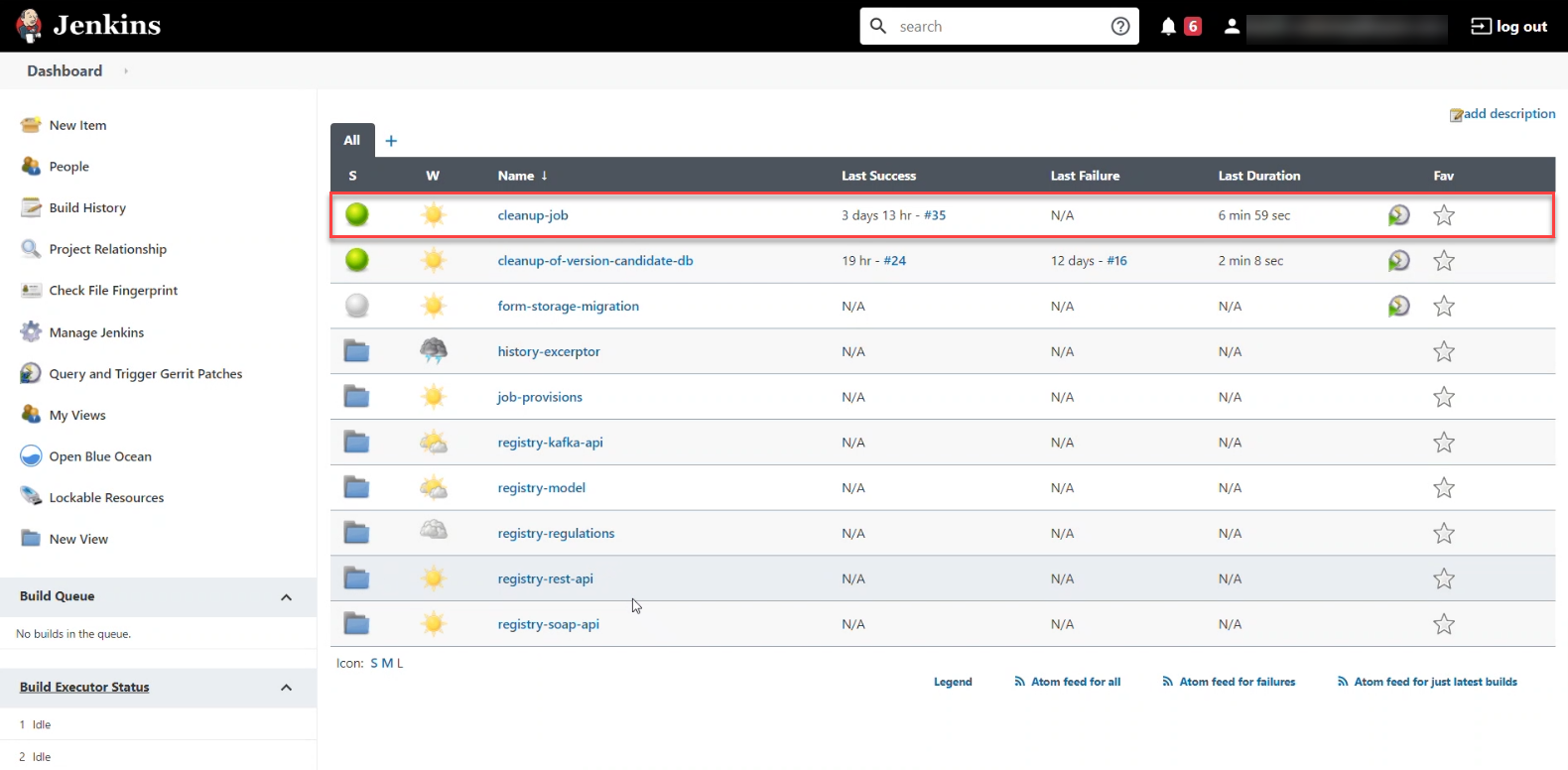
Before starting the cleanup pipeline, you need to specify the parameters to ensure the process works correctly.
All parameters are configured automatically, and changing their configuration is not recommended. The only parameter that needs to be set manually is the DELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYcheckbox that defines the pipeline’s logic.- Here are the parameters with descriptions:
-
-
DELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYdetermines whether the registry-regulations repository should be deleted and re-created from an empty template.If this option is selected, the repository will be deleted and created from scratch. By default, the DELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYoption is cleared. -
STAGEScontains options for configuring the various stages of the process (for details, see Cleanup job stages and steps). -
CODEBASE_NAMEcontains the name of your CodeBase. Set it toregistry-regulations. -
CODEBASE_HISTORY_NAMEcontains the name of CodeBase history that shows the version and state of the code at a certain point in time. Set it tohistory-excerptor. -
REPOSITORY_PATHcontains the path to your repository. This will help the system to find and work with the appropriate repository. -
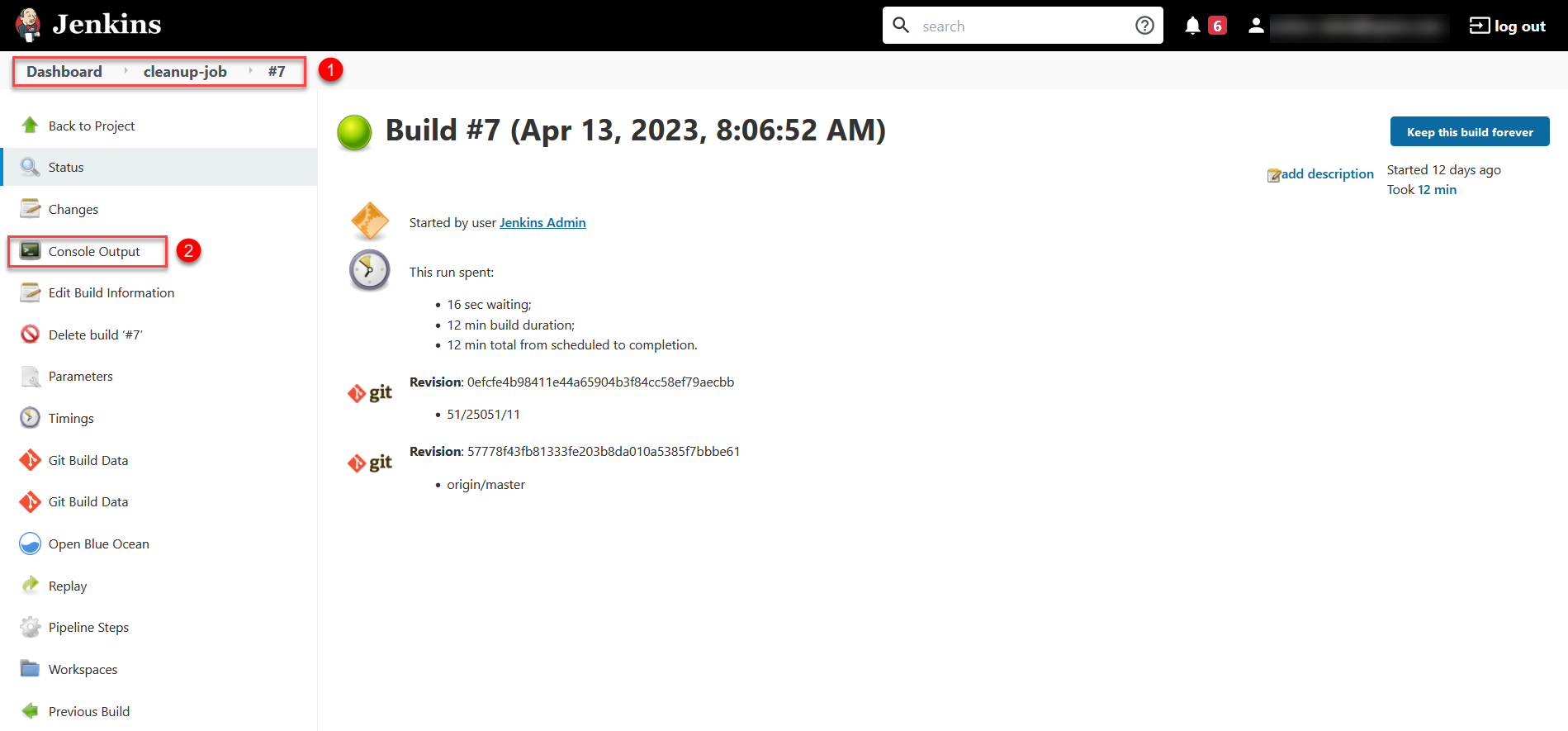
LOG_LEVELdetermines the logging level for the process. Possible values areERROR,WARN,INFO, orDEBUG. This parameter allows you to control the level of detail of information that will be stored in the logs during the execution of the process.To view the process execution log, open the corresponding pipeline and click Console Output in the leftmost menu.
-
DEPLOYMENT_MODEdetermines the system’s deployment mode. Possible values aredevelopmentorproduction.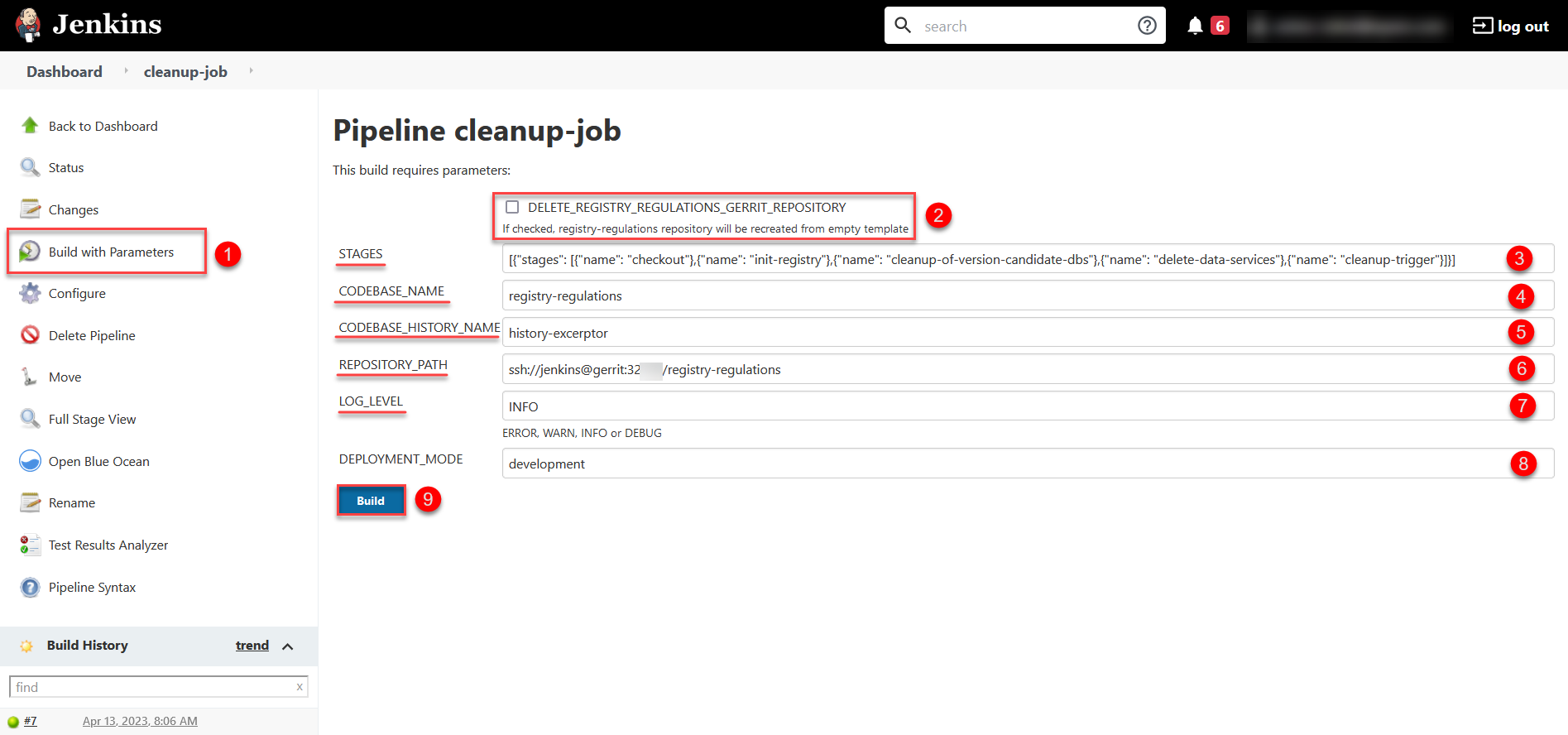
-
-
After setting all parameters, start the cleanup process by clicking the
Buildbutton. The system performs the specified operations according to the configuration and ensures the appropriate state of the codebase and repositories. -
As a result, the regulations cleanup process starts, which either deletes the
registry-regulationsrepository or not, depending on theDELETE_REGISTRY_REGULATIONS_GERRIT_REPOSITORYoption at the cleanup-trigger stage. -
Completing the cleanup process automatically starts the
MASTER-Build-registry-regulationspipeline with theFULL_DEPLOYoption (provided that the cleanup process did not remove theregistry-regulationscomponent), which allows deploying the regulations correctly after the cleanup process.