Add Environment⚓︎
Portal provides the ability to deploy an environment on your own and specify the essential components.
Navigate to the Environments section on the navigation bar and click Create (the plus sign icon on the right side of the screen). Once clicked, the Create CD Pipeline dialog will appear.
The creation of the environment becomes available as soon as an application is created including its provisioning in a branch and the necessary entities for the environment. You can create the environment in YAML or via the three-step menu in the dialog.
Create Environment in YAML ⚓︎
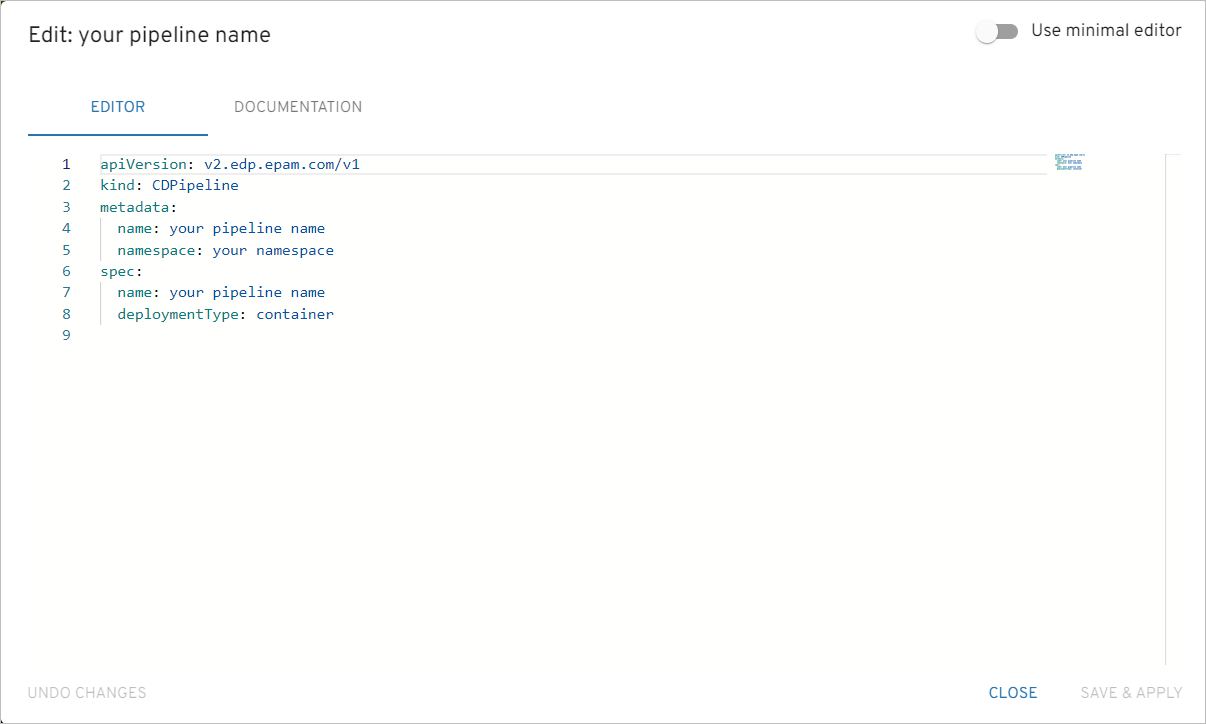
Click Edit YAML in the upper-right corner of the Create CD Pipeline dialog to open the YAML editor and create the environment.
To edit YAML in the minimal editor, turn on the Use minimal editor toggle in the upper-right corner of the Create CD Pipeline dialog.
To save the changes, select the Save & Apply button.
Create Environment in the Dialog ⚓︎
The Create CD Pipeline dialog contains the three steps:
- The Pipeline Menu
- The Applications Menu
- The Stages Menu
The Pipeline Menu⚓︎
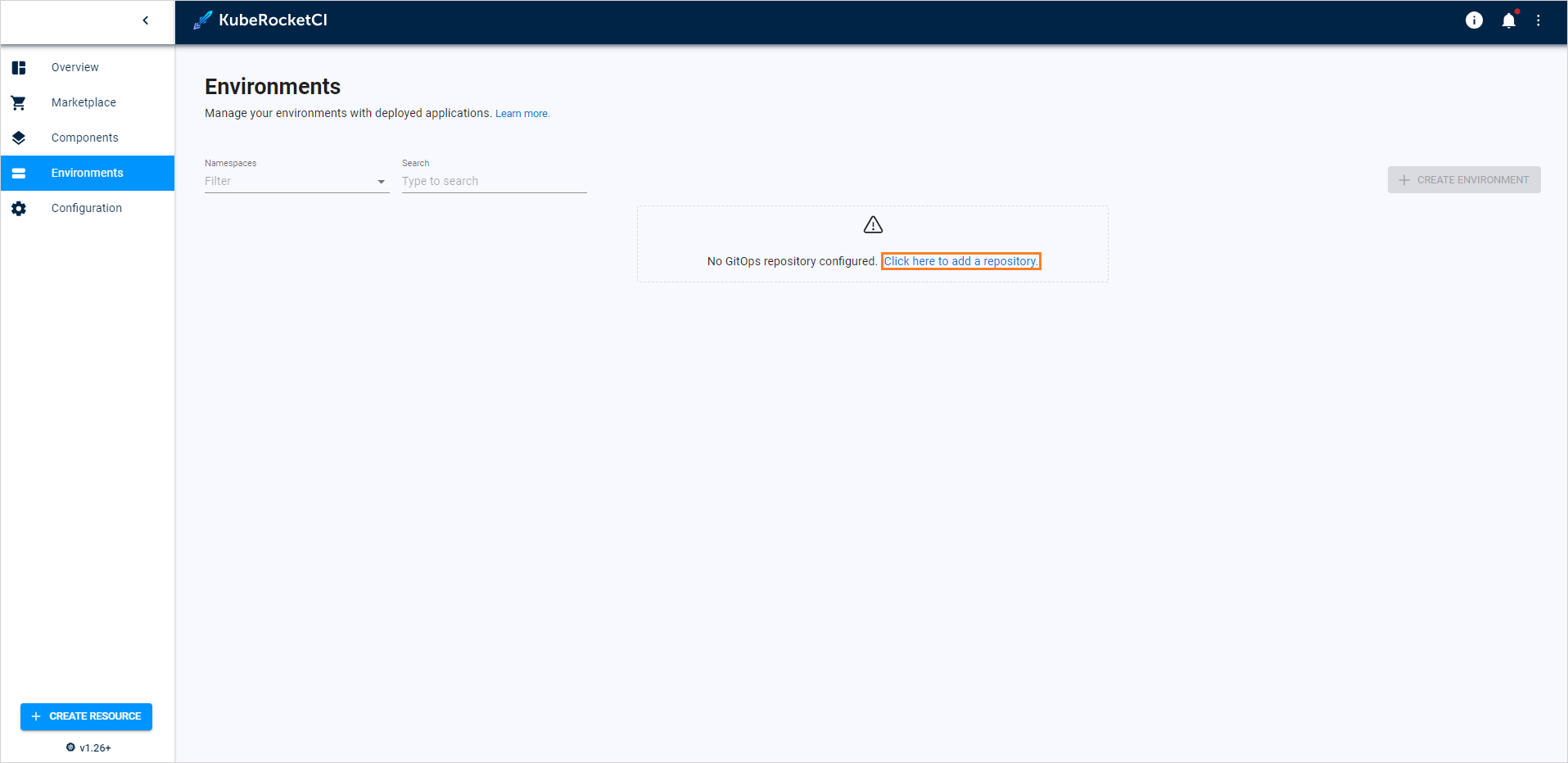
Before proceeding, ensure to familiarize yourself with the Manage GitOps page as it might be required to add a GitOps repository first before creating an environment:
To create an environment, follow the steps below:
-
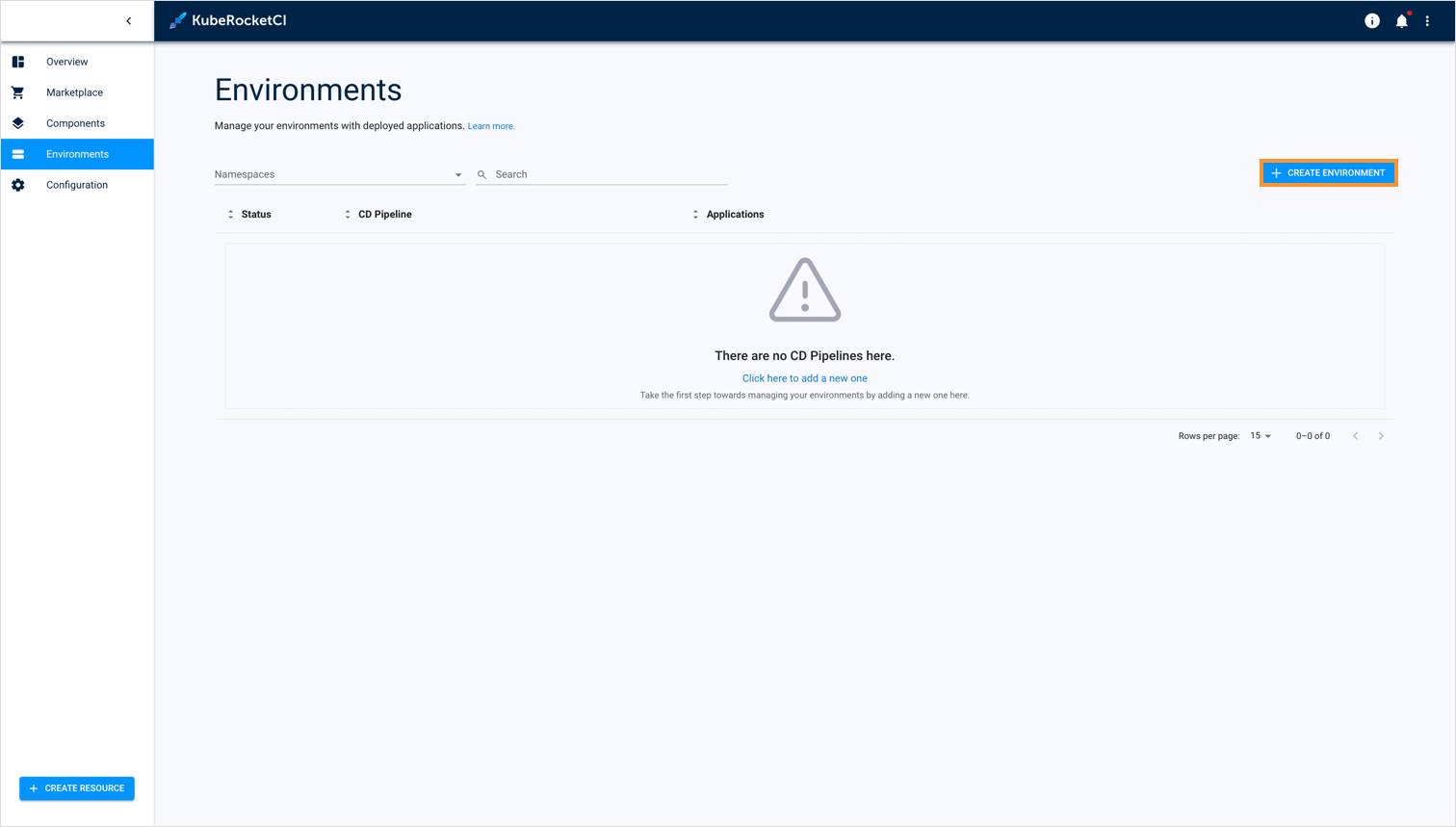
Navigate to the Environments tab and click the + Create Environment button:
-
The Pipeline tab of the Create CD Pipeline menu is presented below:
-
Enter the Environment name that will be displayed in the Environments list.
-
Click the Proceed button to move onto the Applications tab.
-
-
Type the name of the pipeline in the Pipeline Name field by entering at least two characters and by using the lower-case letters, numbers and inner dashes.
Note
The namespace created by the environment has the following pattern combination: [kuberocketci namespace]-[environment name]-[stage name]. Please be aware that the namespace length should not exceed 63 symbols.
-
Select the deployment type from the drop-down list:
- Container - the pipeline will be deployed in a Docker container;
- Custom - this mode allows to deploy non-container applications and customize the Init stage of environment.
-
Click the Proceed button to switch to the next menu.
The Applications Menu⚓︎
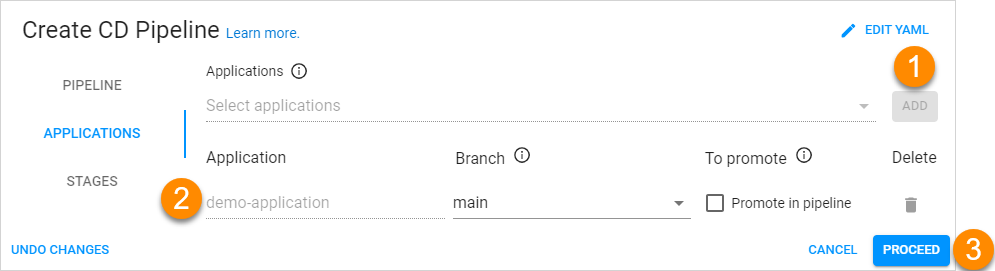
The Pipeline tab of the Create CD Pipeline menu is presented below:
- Select the necessary application from the Mapping field name drop-down menu and click Add.
-
Specify the application parameters:
- Branch - Select the application branch from the drop-down menu.
- Promote in pipeline - Select the this check box in order to transfer the application from one to another stage by the specified codebase Docker branch. If the Promote in pipeline check box is not selected, the same codebase Docker stream will be deployed regardless of the stage, i.e. the codebase Docker stream input, which was selected for the pipeline, will always be used.
Note
If there is another deployed environment stage with the respective codebase Docker stream (= image stream as an OpenShift term), the pattern combination will be as follows: [pipeline name]-[stage name]-[application name]-[verified].
-
Click the Proceed button to switch to the next menu.
The Stages Menu⚓︎
Stages are created the following way:
-
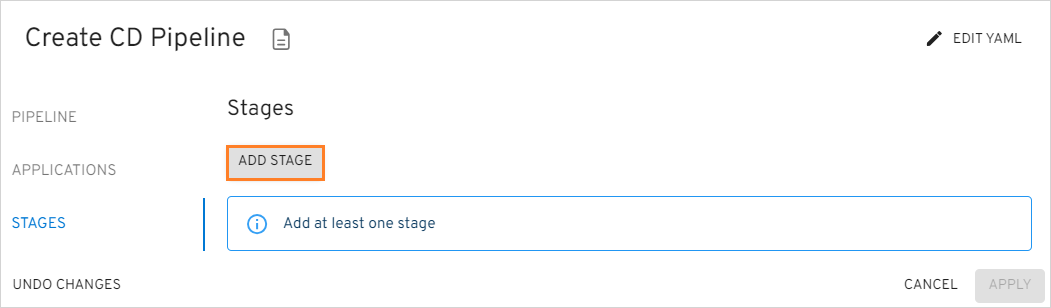
On the Stages menu, click the Add Stage button and fill in the necessary fields in the Adding Stage window :
-
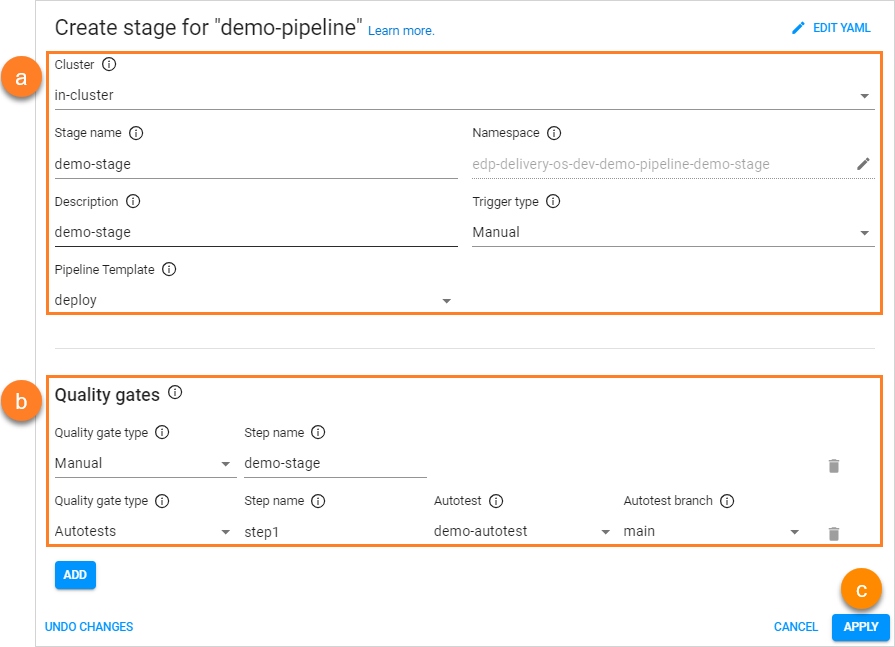
Set the proper cluster options:
- Cluster - Choose the cluster to deploy the stage in;
- Stage name - Enter the stage name;
- Namespace - Specify the Kubernetes namespace where the resources will be deployed in. By default, this field is pre-populated automatically but keep in mind that the namespace name must be no longer than 63 symbols;
- Description - Enter the description for this stage;
-
Trigger type - Select the trigger type. The key benefit of the automatic deploy feature is to keep environments up-to-date. The available trigger types are Manual and Auto. When the Auto trigger type is chosen, the environment will initiate automatically once the image is built. Manual implies that user has to perform deploy manually by clicking the Deploy button in the environment menu. Please refer to the Architecture Scheme of CD Pipeline Operator page for additional details.
Note
Automatic deploy will start working only after the first manual deploy.
- Pipeline template - Choose a predefined blueprint outlining the deployment process for your application. While you have the option to incorporate custom deployment templates by generating a resource of the PipelineTemplate category, you can also opt for one of the preexisting options: with autotests or without.
-
Select the quality gate options:
- Quality gate type - Select the quality gate type:
- Manual - means that the promoting process should be confirmed in Tekton manually;
- Autotests - means that the promoting process should be confirmed by the successful passing of the autotests.;
- Step name - Type the step name, which will be displayed in Tekton, for every quality gate;
- Autotest - Select the previously created autotest name;
- Autotest branch - Specify a branch for the autotest.
Note
Execution sequence. The image promotion and execution of the pipelines depend on the sequence in which the environments are added.
- Quality gate type - Select the quality gate type:
-
Click the Apply button to display the stage in the Stages menu.
-
-
Click the Apply button to start the provisioning of the pipeline.
As a result, a new environment will be created in the environments list.