Logsight Integration⚓︎
Logsight can be integrated with the CI/CD pipeline. It connects to log data sources, analyses collected logs, and evaluates deployment risk scores.
Overview⚓︎
In order to understand if a microservice or a component is ready for the deployment, EDP suggests analyzing logs via Logsight to decide if the deployment is risky or not.
Please find more about Logsight in the official documentation:
Logsight as a Quality Gate⚓︎
Integration with Logsight allows enhancing and optimizing software releases by creating an additional quality gate.
Logsight can be configured in two ways:
- SAAS - online system; for this solution a connection string is required.
- Self-deployment - local installation.
To work with Logsight, a new Deployment Risk stage must be added to the pipeline. On this stage, the logs are analyzed with the help of Logsight mechanisms.
On the verification screen of Logsight, continuous verification of the application deployment can be monitored, and tests can be compared for detecting test flakiness.
For example, two versions of a microservice can be compared in order to detect critical differences. Risk score will be calculated for the state reached by version A and version B. Afterwards, the deployment risk will be calculated based on individual risk scores.
If the deployment failure risk is greater than a predefined threshold, the verification gate blocks the deployment from going to the target environment. In such case, the Deployment Risk stage of the pipeline is not passed, and additional attention is required. The exact log messages can be displayed in the Logsight verification screen, to help debug the problem.
Use Logsight for EDP Development⚓︎
Please find below the detailed description of Logsight integration with EDP.
Deployment Approach⚓︎
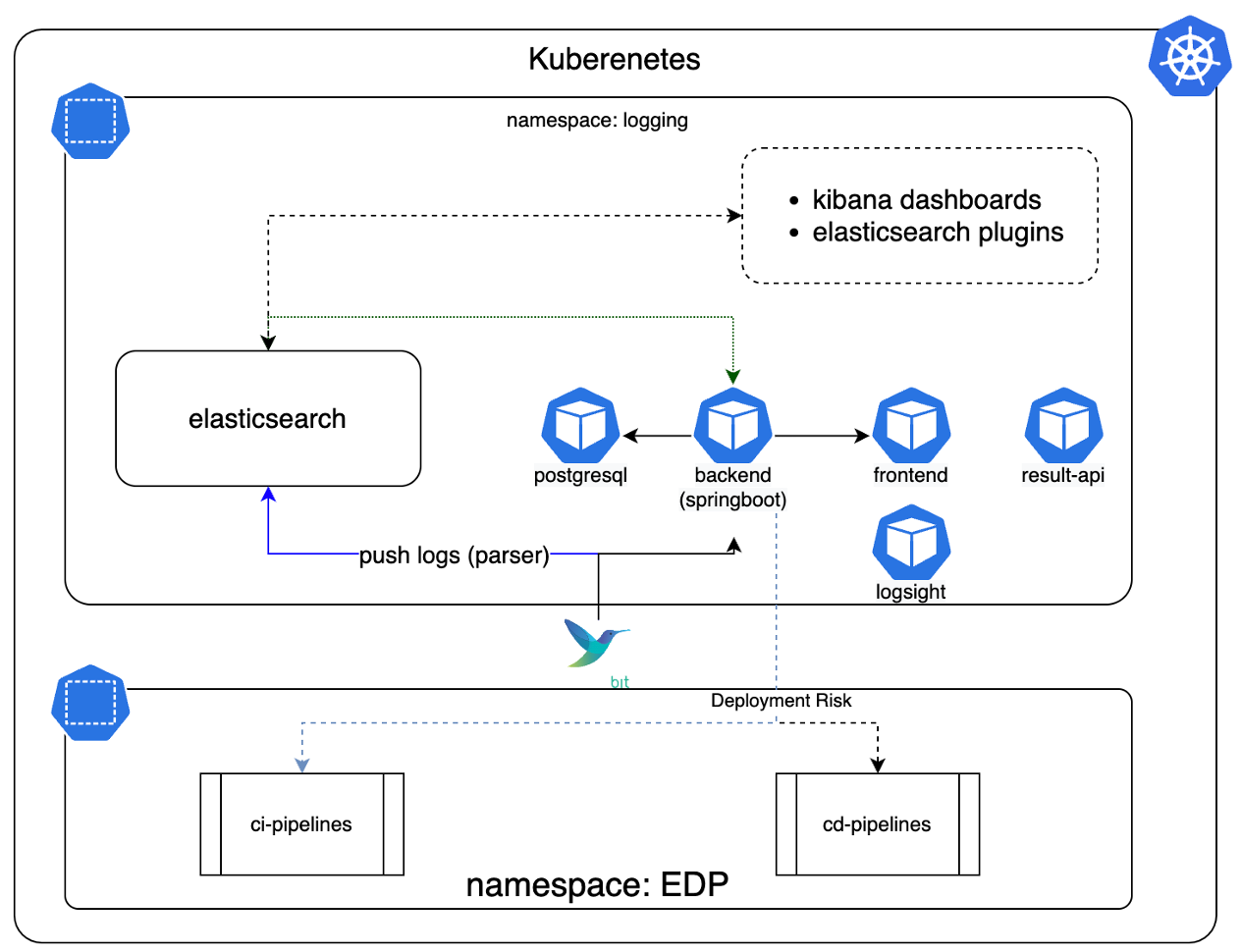
EDP uses Logsight in a self-deploying mode.
Logsight provides a deployment approach using Helm charts. Please find below the stack of components that must be deployed:
logsight- the core component.logsight-backend- the backend that provides all necessary APIs and user management.logsight-frontend- the frontend that provides the user interface.logsight-result-api- responsible for obtaining results, for example, during the verification.
Below is a diagram of interaction when integrating the components:
Configure FluentBit for Sending Log Data⚓︎
Logsight is integrated with the EDP logging stack. The integration is based on top of the EFK (ElasticSearch-FluentBit-Kibana) stack. It is necessary to deploy a stack with the security support, namely, enable the certificate support.
A FluentBit config indicates the namespace from which the logs will be received for further analysis. Below is an example of the FluentBit config for getting logs from the edp-delivery-edp-delivery-sit namespace:
View: fluent-bit.conf
[INPUT]
Name tail
Tag kube.sit.*
Path /var/log/containers/*edp-delivery-edp-delivery-sit*.log
Parser docker
Mem_Buf_Limit 5MB
Skip_Long_Lines Off
Refresh_Interval 10
[FILTER]
Name kubernetes
Match kube.sit.*
Kube_URL https://kubernetes.default.svc:443
Kube_CA_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
Kube_Token_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
Kube_Tag_Prefix kube.sit.var.log.containers.
Merge_Log Off
K8S-Logging.Parser On
K8S-Logging.Exclude On
[FILTER]
Name nest
Match kube.sit.*
Operation lift
Nested_under kubernetes
Add_prefix kubernetes.
[FILTER]
Name modify
Match kube.sit.*
Copy kubernetes.container_name tags.container
Copy log message
Copy kubernetes.container_image tags.image
Copy kubernetes.namespace_name tags.namespace
[FILTER]
Name nest
Match kube.sit.*
Operation nest
Wildcard kubernetes.*
Nested_under kubernetes
Remove_prefix kubernetes.
[OUTPUT]
Name es
Match kube.sit.*
Host elasticsearch-master
Port 9200
HTTP_User elastic
HTTP_Passwd *****
Logstash_Format On
Logstash_Prefix sit
Time_Key @timestamp
Type flb_type
Replace_Dots On
Retry_Limit False
[OUTPUT]
Match kube.sit.*
Name http
Host logsight-backend
Port 8080
http_User logsight@example.com
http_Passwd *****
uri /api/v1/logs/singles
Format json
json_date_format iso8601
json_date_key timestamp
Deployment Risk Analysis⚓︎
A deployment-risk stage is added to the EDP CD pipeline.
If the deployment risk is above 70%, the red state of the pipeline is expected.
EDP consists of a set of containerized components. For the convenience of tracking the risk deployment trend for each component, this data is stored as Jenkins artifacts.
If the deployment risk is higher than the threshold of 70%, the EDP promotion of artifacts for the next environments does not pass. The deployment risk report can be analyzed in order to avoid the potential problems with updating the components.
To study the report in detail, use the link from the Jenkins pipeline to the Logsight verification screen:
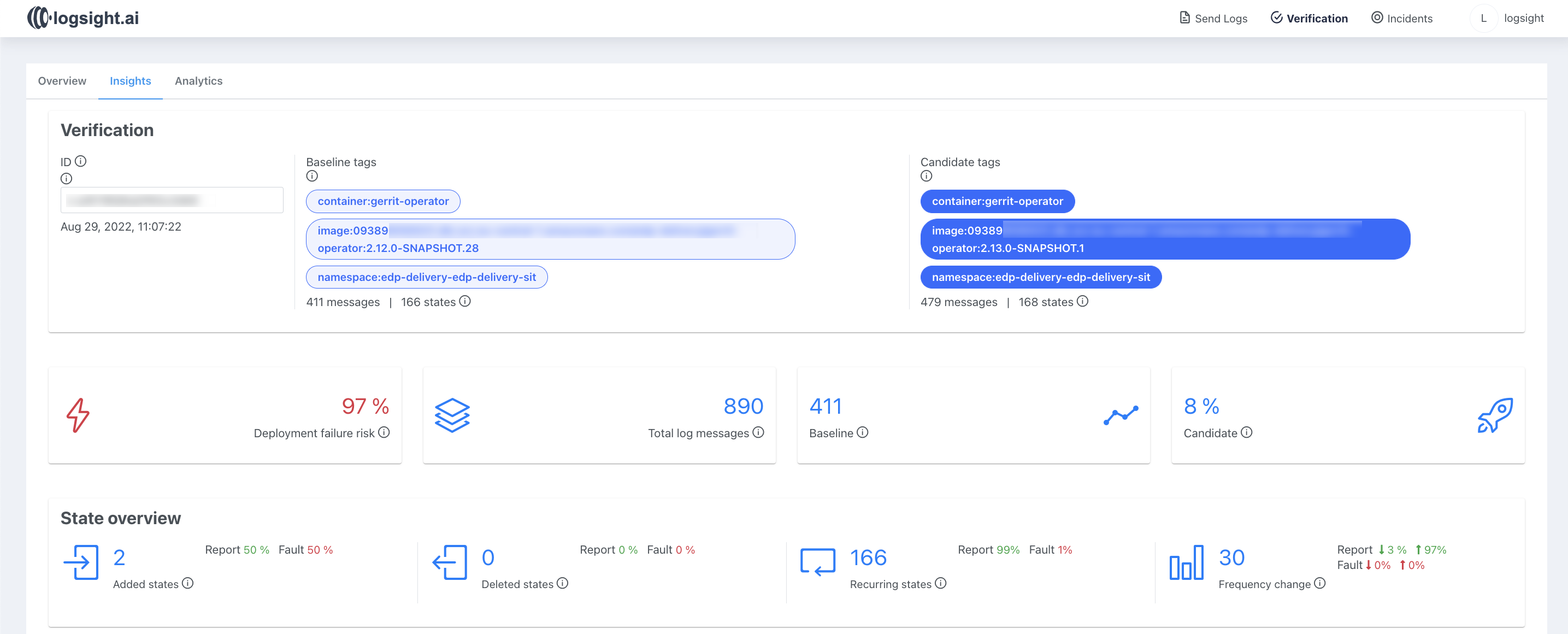
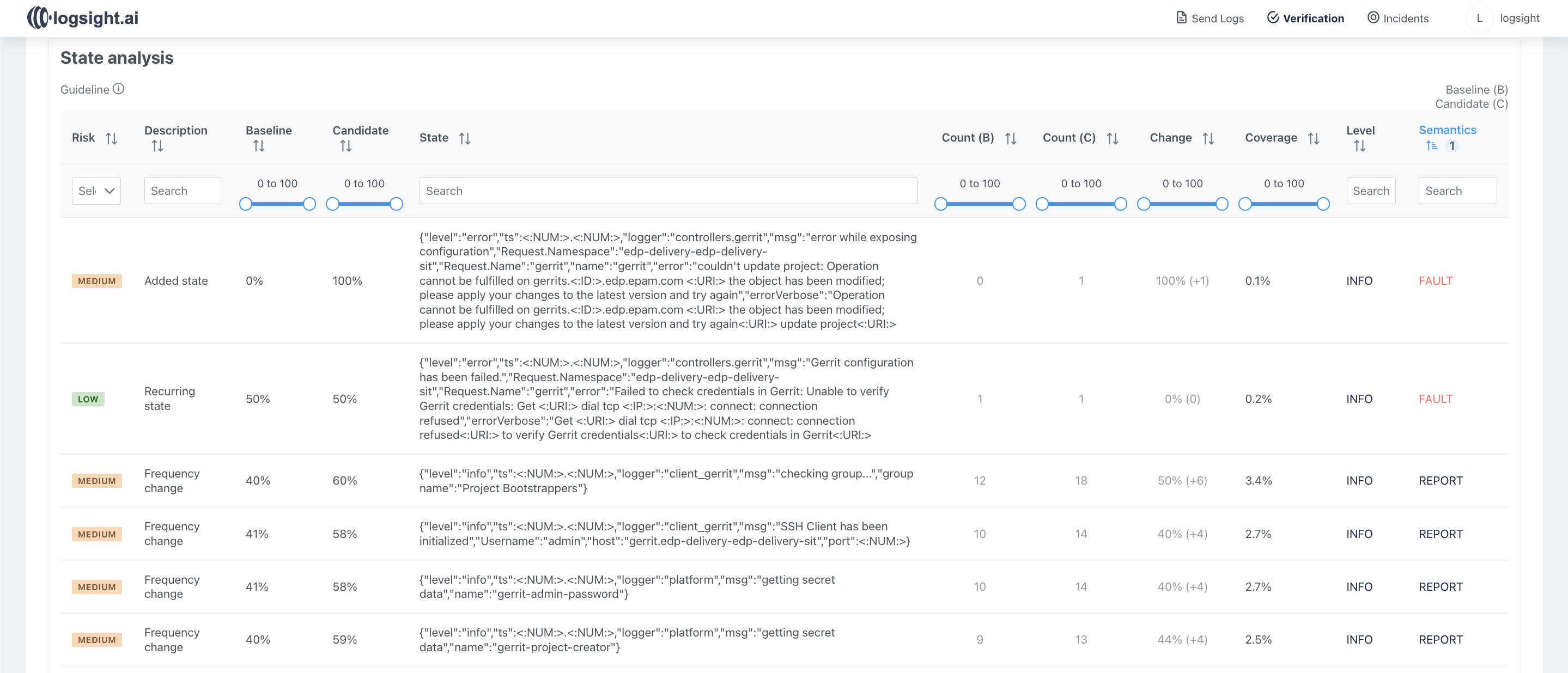
In this example, logs from different versions of the gerrit-operator were analyzed. As can be seen from the report, a large number of new messages appeared in the logs, and the output frequency of other notifications has also changed, which led to the high deployment risk.
The environment on which the analysis is performed can exist for different time periods. Logsight only processes the minimum total number of logs since the creating of the environment.