Argo CD Integration⚓︎
KubeRocketCI uses Argo CD as a part of the Continues Delivery/Continues Deployment implementation. Argo CD follows the best GitOps practices, uses Kubernetes native approach for the Deployment Management, has rich UI and required RBAC capabilities.
Argo CD Deployment Approach in KubeRocketCI⚓︎
Argo CD can be installed using two different approaches:
- Cluster-wide scope with the cluster-admin access
- Namespaced scope with the single namespace access
Both approaches can be deployed with High Availability (HA) or Non High Availability (non HA) installation manifests.
KubeRocketCI uses the HA deployment with the cluster-admin permissions, to minimize cluster resources consumption by sharing single Argo CD instance across multiple EDP Tenants. Please follow the installation instructions to deploy Argo CD.
Argo CD Integration⚓︎
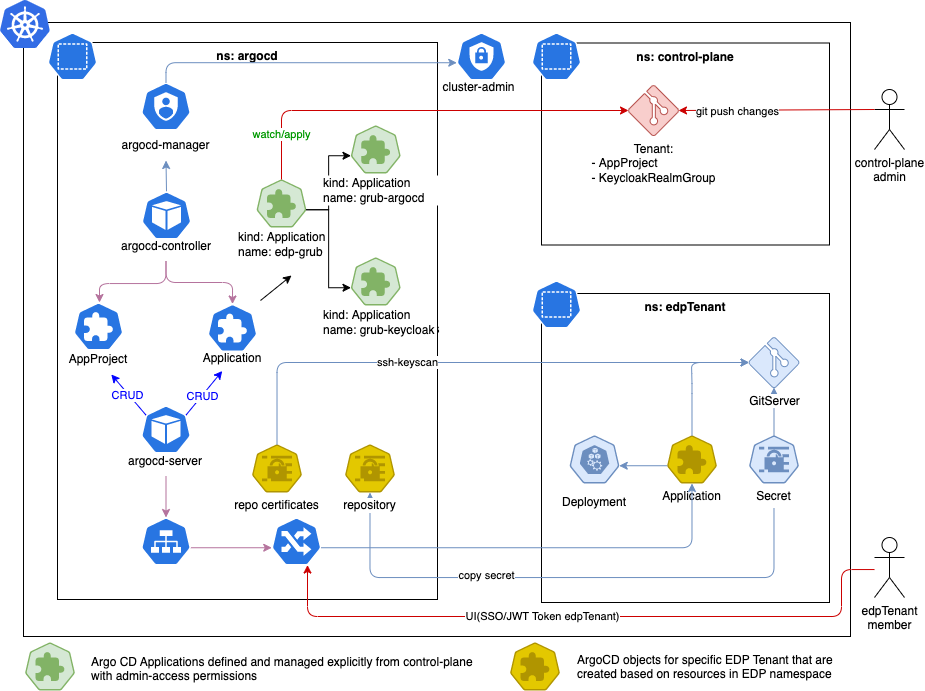
See a diagram below for the details:
- Argo CD is deployed in a separate
argocdnamespace. - Argo CD uses a
cluster-adminrole for managing cluster-scope resources. - The
control-planeapplication is created using the App of Apps approach, and its code is managed by thecontrol-planemembers. - The
control-planeis used to onboard new Argo CD Tenants (Argo CD Projects - AppProject). - The
EDP Tenant MembermanagesArgo CD Applicationsusingkind: Applicationin theedpTenantnamespace.
The App Of Apps approach is used to manage the EDP Tenants. Inspect the edp-grub repository structure that is used to provide the EDP Tenants for the Argo CD Projects:
edp-grub
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── apps ### All Argo CD Applications are stored here
│ ├── grub-argocd.yaml # Application that provisions Argo CD Resources - Argo Projects (EDP Tenants)
│ └── grub-keycloak.yaml # Application that provisions Keycloak Resources - Argo CD Groups (EDP Tenants)
├── apps-configs
│ └── grub
│ ├── argocd ### Argo CD resources definition
│ │ └── edp.yaml
│ └── keycloak ### Keycloak resources definition
│ └── edp.yaml
├── bootstrap
│ └── root.yaml ### Root application in App of Apps, which provision Applications from /apps
└── examples ### Examples
└── tenant
└── edp-petclinic.yaml
The Root Application must be created under the control-plane scope.
Argo CD Configuration⚓︎
Now that Argo CD is integrated, it is time to configure it properly. To configure Argo CD for KubeRocketCI, follow the steps below:
-
Modify the
argocd-cmd-params-cmConfigMap in theargocdnamespace and add theapplication.namespacesparameter to the subsection data: -
Add a credential template for GitHub, GitLab, Gerrit integrations. The credential template must be created for each Git server.
Generate an SSH key pair and add a public key to GitLab or GitHub account.
Warning
Use an additional GitHub/GitLab User to access a repository.
For example:
- GitHub, add a User to a repository with a "Read" role.
- GitLab, add a User to a repository with a "Guest" role.Copy SSH private key to Argo CD namespace
EDP_NAMESPACE="edp" VCS_HOST="<github.com_or_gitlab.com>" ACCOUNT_NAME="<ACCOUNT_NAME>" URL="ssh://git@${VCS_HOST}:22/${ACCOUNT_NAME}" kubectl create secret generic ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -n argocd \ --from-file=sshPrivateKey=argocd \ --from-literal=url="${URL}" kubectl label --overwrite secret ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -n argocd "argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type=repo-creds"Add public SSH key to GitHub/GitLab account.
Copy existing SSH private key for Gerrit to Argo CD namespace
EDP_NAMESPACE="edp" GERRIT_PORT=$(kubectl get gerrit gerrit -n ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -o jsonpath='{.spec.sshPort}') GERRIT_ARGOCD_SSH_KEY_NAME="gerrit-ciuser-sshkey" GERRIT_URL=$(echo "ssh://edp-ci@gerrit.${EDP_NAMESPACE}:${GERRIT_PORT}" | base64) kubectl get secret ${GERRIT_ARGOCD_SSH_KEY_NAME} -n ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -o json | jq 'del(.data.username,.metadata.annotations,.metadata.creationTimestamp,.metadata.labels,.metadata.resourceVersion,.metadata.uid,.metadata.ownerReferences)' | jq '.metadata.namespace = "argocd"' | jq --arg name "${EDP_NAMESPACE}" '.metadata.name = $name' | jq --arg url "${GERRIT_URL}" '.data.url = $url' | jq '.data.sshPrivateKey = .data.id_rsa' | jq 'del(.data.id_rsa,.data."id_rsa.pub")' | kubectl apply -f - kubectl label --overwrite secret ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -n argocd "argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type=repo-creds" -
Add SSH Known hosts for Gerrit, GitHub, GitLab integration.
Add GitHub/GitLab host to Argo CD config map with known hosts
EDP_NAMESPACE="edp" VCS_HOST="<VCS_HOST>" KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE="/tmp/ssh_known_hosts" ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME="argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm" rm -f ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} kubectl get cm ${ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME} -n argocd -o jsonpath='{.data.ssh_known_hosts}' > ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} ssh-keyscan ${VCS_HOST} >> ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} kubectl create configmap ${ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME} -n argocd --from-file ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl apply -f -Add Gerrit host to Argo CD config map with known hosts
EDP_NAMESPACE="edp" KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE="/tmp/ssh_known_hosts" ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME="argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm" GERRIT_PORT=$(kubectl get gerrit gerrit -n ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -o jsonpath='{.spec.sshPort}') rm -f ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} kubectl get cm ${ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME} -n argocd -o jsonpath='{.data.ssh_known_hosts}' > ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} kubectl exec -it deployment/gerrit -n ${EDP_NAMESPACE} -- ssh-keyscan -p ${GERRIT_PORT} gerrit.${EDP_NAMESPACE} >> ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} kubectl create configmap ${ARGOCD_KNOWN_HOSTS_NAME} -n argocd --from-file ${KNOWN_HOSTS_FILE} -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl apply -f - -
Create an Argo CD Project (EDP Tenant), for example, with the
edpname:AppProjectapiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: AppProject metadata: name: edp namespace: argocd # Finalizer that ensures that project is not deleted until it is not referenced by any application finalizers: - resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io spec: destinations: # by default edp work with 'edp-*' namespace - namespace: 'edp-*' # allow to deploy to specific server (local in our case) name: in-cluster # Deny all cluster-scoped resources from being created, except for Namespace clusterResourceWhitelist: - group: '' kind: Namespace # Allow all namespaced-scoped resources to be created, except for ResourceQuota, LimitRange, NetworkPolicy namespaceResourceBlacklist: - group: '' kind: ResourceQuota - group: '' kind: LimitRange - group: '' kind: NetworkPolicy # we are ok to create any resources inside namespace namespaceResourceWhitelist: - group: '*' kind: '*' # enable access only for specific git server. The example below 'edp' - it is namespace where EDP deployed sourceRepos: - ssh://git@github.com/* # enable capability to deploy objects from namespaces sourceNamespaces: - edp -
Check that your new Repository, Known Hosts, and AppProject are added to the Argo CD UI.
-
Generate Argo CD project token for deploy integration:
URL=<ARGO CD URL> TOKEN=$(argocd proj role create-token edp developer -i argocd-ci -t) cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: argocd-ci namespace: edp labels: app.edp.epam.com/integration-secret: "true" app.edp.epam.com/secret-type: "argocd" type: Opaque stringData: token: $TOKEN url: $URL EOF
Once Argo CD is successfully integrated, EDP user can utilize Argo CD to deploy CD pipelines.
Check Argo CD Integration (Optional)⚓︎
This section provides the information on how to test the integration with Argo CD and is not mandatory to be followed.
-
Add an Argo CD application:
Example: Argo CD Application
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: demo spec: project: edp destination: namespace: edp-demo server: https://kubernetes.default.svc source: helm: parameters: - name: image.tag value: master-0.1.0-1 - name: image.repository value: image-repo path: deploy-templates # github/gitlab example ssh://git@github.com/<github_account_name>/<repository_name>.git # gerrit example ssh://<gerrit_user>@gerrit.edp:30007/<repository_name>.git repoURL: ssh://git@github.com/edp/demo.git targetRevision: master syncPolicy: syncOptions: - CreateNamespace=true automated: selfHeal: true prune: true -
Check that your new Application is added to the Argo CD UI under the
edpProject scope.
Deploy Argo CD Application to Remote Cluster (Optional)⚓︎
KubeRocketCI also supports deploying Argo CD applications to a remote cluster. To deploy applications to remote clusters, follow the steps below:
-
Create
ServiceAccountClusterRoleBindingandSecretfor thatServiceAccount. -
Receive the bearer token:
-
Create ArgoCD secret for remote cluster:
manifestapiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: edp-remote-cluster namespace: argocd data: # Remote cluster config config: {"bearerToken":"<BEAR_TOKEN>","tlsClientConfig":{"insecure":false,"caData":"<certificate-authority-data>"}} # Remote cluster name name: "edp-remote-cluster" # Cluster endpoint URL server: "https://xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.sk1.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com" type: stringData -
Update an Argo CD Project (EDP Tenant), with the
edpname: -
Add a remote cluster in the KubeRocketCI portal. Please refer to the Add Cluster page for details.
Keycloak Integration (Optional)⚓︎
Note
To proceed with the steps below, you need the edp-keycloak-operator to be deployed.
To provide Argo CD with the Keycloak SSO authorization mechanism, follow the guidelines below:
-
Create secret
keycloak-client-argocd-secret. -
Update the
argocd-cmConfigMap:data: oidc.config: url: "https://argocd.<.Values.global.dnsWildCard>" application.instanceLabelKey: argocd.argoproj.io/instance-edp oidc.config: | name: Keycloak issuer: https://<.Values.global.keycloakEndpoint>/auth/realms/edp clientID: argocd-tenant clientSecret: $keycloak-client-argocd-secret:clientSecret requestedScopes: - openid - profile - email - groups -
Create a Keycloak Group:
-
Create a Keycloak Client:
apiVersion: v1.edp.epam.com/v1 kind: KeycloakClient metadata: name: argocd namespace: argocd spec: advancedProtocolMappers: true attributes: post.logout.redirect.uris: + clientId: argocd-tenant defaultClientScopes: - groups realmRef: kind: ClusterKeycloakRealm name: main secret: keycloak-client-argocd-secret webUrl: "https://argocd.<.Values.global.dnsWildCard>" -
In Keycloak, add users to the
ArgoCD-edp-usersKeycloak Group. -
Update spec in project:
AppProjectspec: description: CD pipelines for edp roles: - name: developer description: Users for edp tenant policies: - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, create, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, delete, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, get, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, override, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, sync, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, applications, update, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, repositories, create, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, repositories, delete, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, repositories, update, edp/*, allow - p, proj:edp:developer, repositories, get, edp/*, allow groups: # Keycloak Group name - ArgoCD-edp-users -
Then restart the deployment: